The post Announcing ScaleOut In-Memory Database: Automated Clustering for Redis Users appeared first on ScaleOut Software.
]]>
ScaleOut Software is excited to announce the release of ScaleOut In-Memory Database , which offers a new, highly scalable, clustered server platform for running Redis commands. This platform uses ScaleOut’s patented, quorum-based clustering technology to replace open-source Redis’s cluster implementation. It fully automates Redis cluster management while preserving the use of open-source Redis code to process commands. In doing so, ScaleOut In-Memory Database lets enterprise Redis users manage server clusters with much greater ease and lower both their acquisition and management costs (TCO) — while preserving a native execution environment for Redis applications. ScaleOut In-Memory Database runs on both Linux and Windows systems.
, which offers a new, highly scalable, clustered server platform for running Redis commands. This platform uses ScaleOut’s patented, quorum-based clustering technology to replace open-source Redis’s cluster implementation. It fully automates Redis cluster management while preserving the use of open-source Redis code to process commands. In doing so, ScaleOut In-Memory Database lets enterprise Redis users manage server clusters with much greater ease and lower both their acquisition and management costs (TCO) — while preserving a native execution environment for Redis applications. ScaleOut In-Memory Database runs on both Linux and Windows systems.
What sets ScaleOut’s cluster architecture apart
When ScaleOut Software first developed its clustering technology for scalable in-memory data storage in 2003, we had to tackle several technical challenges. We needed to:
- implement a scalable cluster membership,
- partition the in-memory data store across multiple servers,
- replicate updates with zero data loss (i.e., avoid eventual consistency), and
- maximize throughput with multi-threading on multicore servers.
We also realized that it was important not to expose all these complexities to users. The cluster had to be easy to manage, making a simple learning curve for system administrators. It was also vital to have a straightforward view of the data store for applications (that is, maintain location transparency and full consistency) so developers could target it easily.
Automated clustering
Our clustering architecture has many leading-edge automated clustering features. These include the ability to:
- self-organize multiple servers into a cluster,
- automatically partition data and distribute it across the cluster,
- load-balance stored data as servers are added or removed,
- automatically create and maintain replicas,
- detect server and network failures,
- recover from failures by promoting replicas to replace failed primary partitions, and
- “self-heal” by creating new replicas to replace lost ones.
Stability and consistency
The server cluster uses peer-to-peer algorithms to avoid single points of failure. Running on one or more servers, it maintains availability to applications even if all but one server fails. It uses a patented quorum algorithm to implement full (strong) consistency when updating stored data across multiple servers. Lastly, it executes multiple requests at once using a multi-threaded architecture.
Industry-leading ease of use
ScaleOut’s cluster architecture does all this without showing its inner workings to developers or system administrators. Developers see a single, reliable data store that happens to be distributed across multiple servers. System administrators see a set of servers on a single network subnet, each running a single service process.
Once the service is configured to select a specific subnet (if multiple NICs are in use), it joins the cluster with one click and is ready to take on its share of the workload. Building a server cluster is just a matter of adding servers (called “nodes” in Redis documentation):
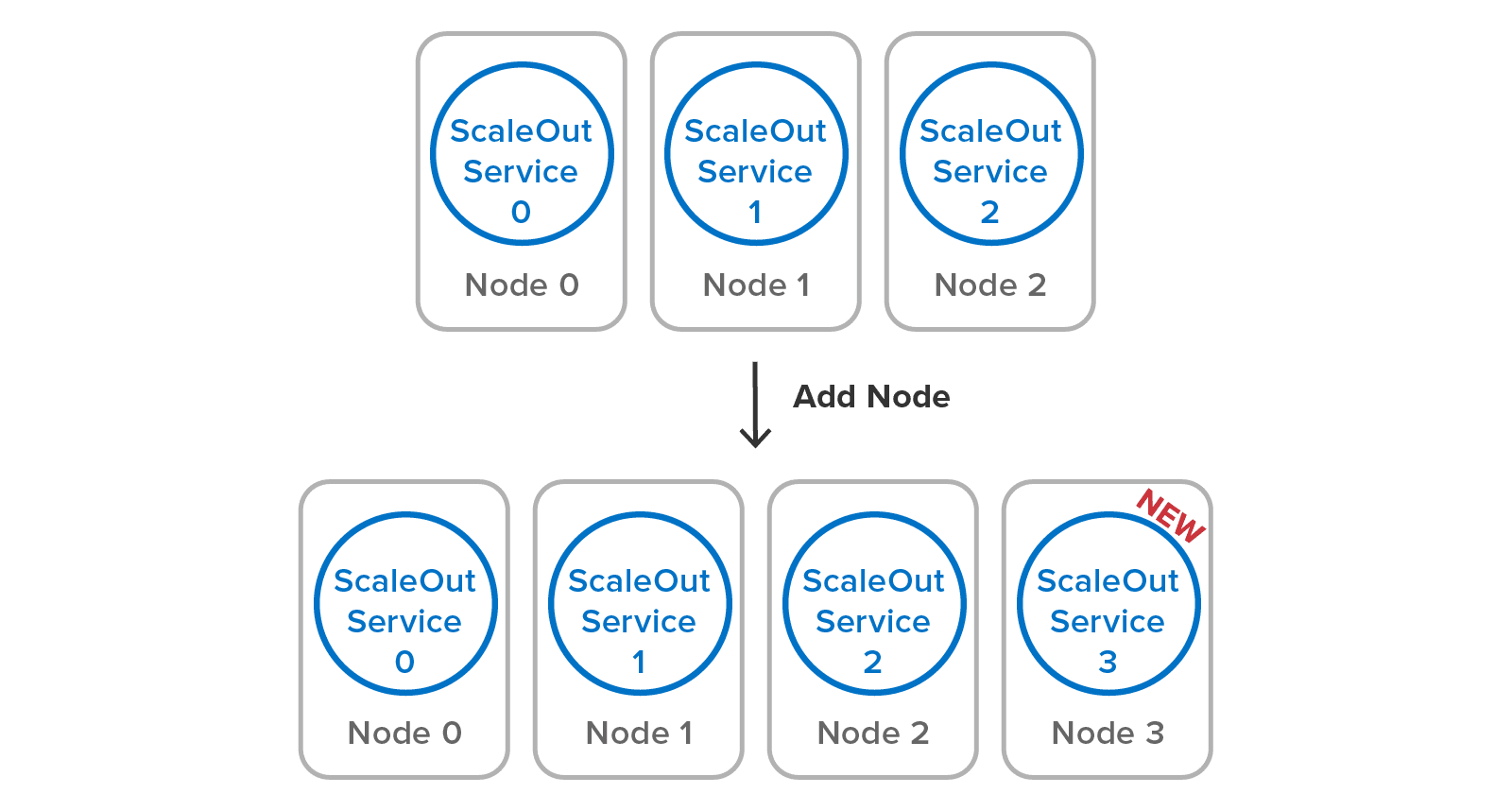 All this automation minimizes the workload for system administrators, lowering costs and increasing uptime. Administrators are unaware of the cluster’s data partitioning mechanism and replica placement. They don’t need to intervene to recover and heal the data store if a server fails or becomes isolated. They also don’t need to spin up multiple service processes per node to extract more throughput from multicore servers.
All this automation minimizes the workload for system administrators, lowering costs and increasing uptime. Administrators are unaware of the cluster’s data partitioning mechanism and replica placement. They don’t need to intervene to recover and heal the data store if a server fails or becomes isolated. They also don’t need to spin up multiple service processes per node to extract more throughput from multicore servers.
Enter Redis
Open-source Redis was first created in 2009 for use on a single server, with clustering added in 2015. It has gained widespread popularity because of its rich set of data structures and commands. At the enterprise level, it has seen fast-growing adoption across many applications. As a result, the need to streamline cluster management procedures and increase data reliability for Redis users has become more urgent.
Introducing automated Redis clustering with ScaleOut In-Memory Database
We created ScaleOut In-Memory Database to meet this need. This product integrates open-source Redis code (version 6.2.5) that implements all the popular Redis data structures (strings, lists, sets, hashes, streams, and more) into ScaleOut’s automated cluster architecture and execution platform. Now, system administrators don’t need to manage Redis concepts like hashslots and shards. Instead, ScaleOut takes over these tasks using its built-in, fully automated mechanisms. Automated recovery and self-healing eliminate the need for manual intervention and increase uptime. What’s more, ScaleOut’s quorum-based updates replace Redis’s eventual consistency mechanism to deliver reliable data storage across servers. Applications can depend on the server cluster to survive a server failure without data loss, and the cluster remains available even if multiple servers fail.
To boost throughput and automatically make full use of all available processing cores, ScaleOut In-Memory Database integrates Redis command execution with its multi-threaded processing of client requests. Achieving this meant eliminating Redis’s native, single-threaded event-loop execution model without introducing a global lock that would constrain performance. The result is that each server in the cluster can run Redis commands simultaneously on all processing cores using a single service process.
Power with simplicity
We designed ScaleOut’s peer-to-peer cluster architecture to serve as the foundation for all user services. Hence, functions like clearing the database and backup/restore were built from the outset to run in parallel across all servers. This approach reduces the system administrator’s workload and delivers fast performance. To give Redis users the benefit of a fully parallel architecture, ScaleOut In-Memory Database provides a cluster-wide implementation of many Redis commands, such as PUBLISH and FLUSHALL.
ScaleOut In-Memory Database also overcomes the single-server limitation of the Redis SAVE command. It provides a cluster-wide implementation of backup/restore using its built-in parallel backup/restore utility. This allows system administrators to backup all Redis objects with one click in ScaleOut’s management console, and it delivers parallel speedup by running simultaneously on all servers. The user can backup either to local disks:
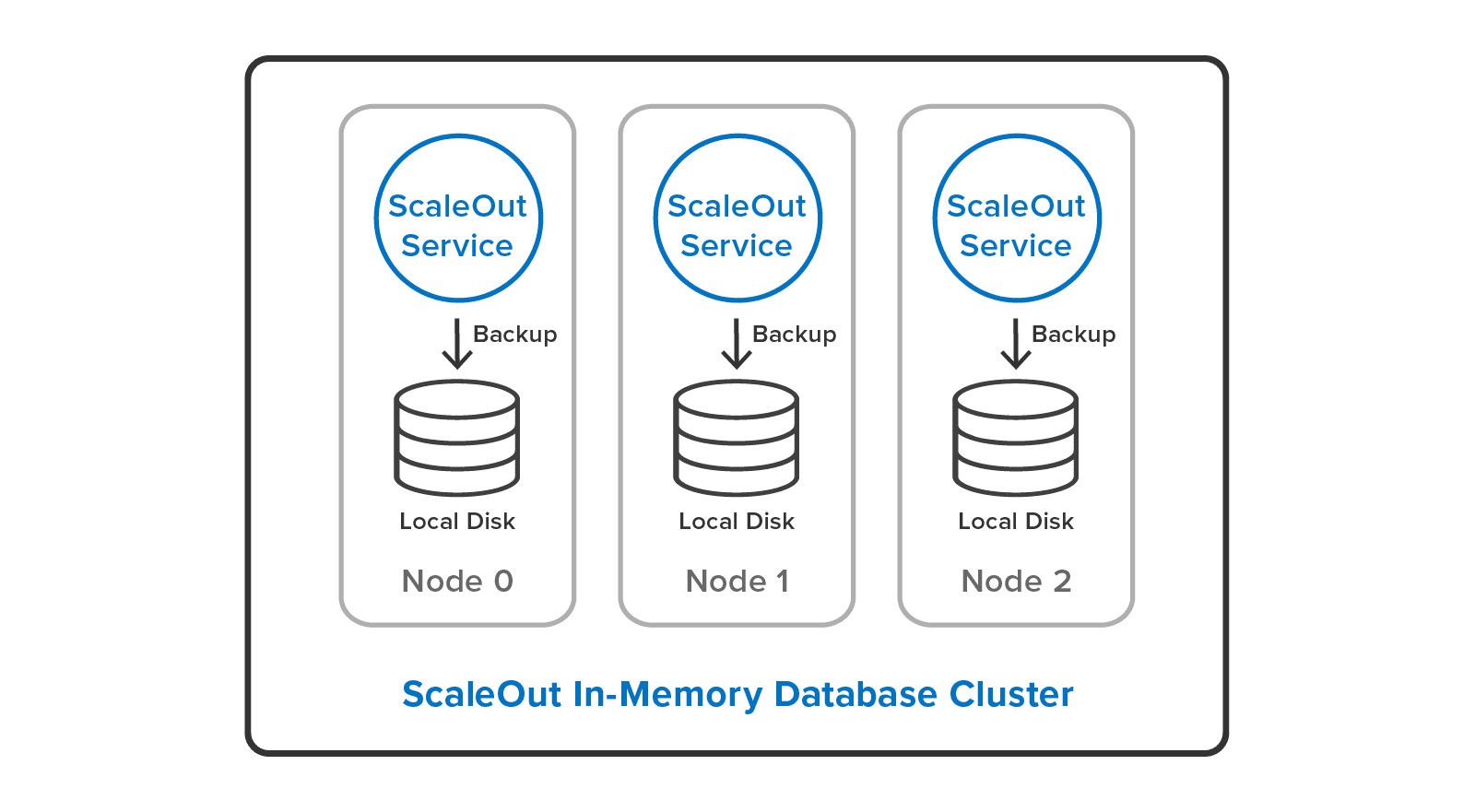
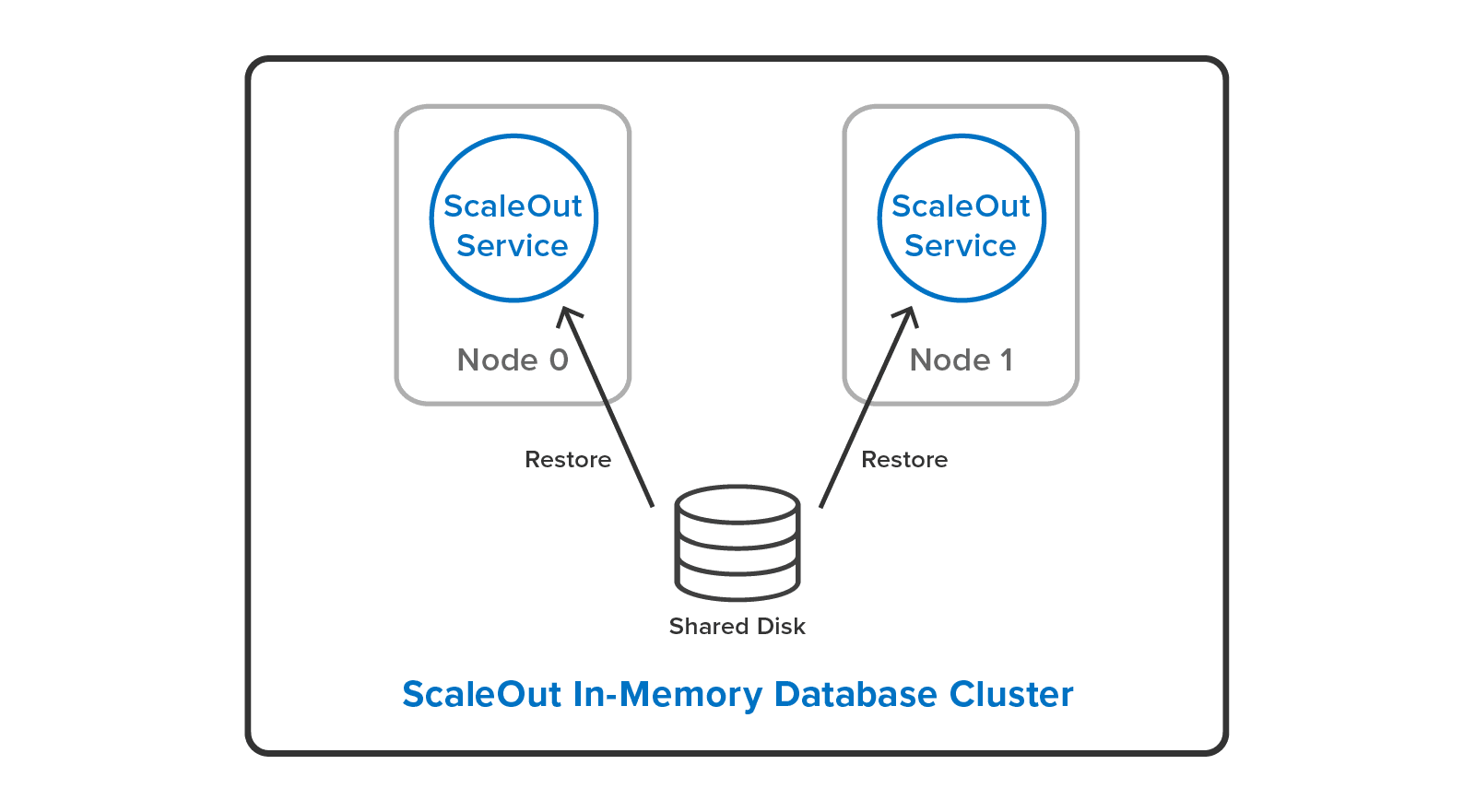
or to a single, shared disk:
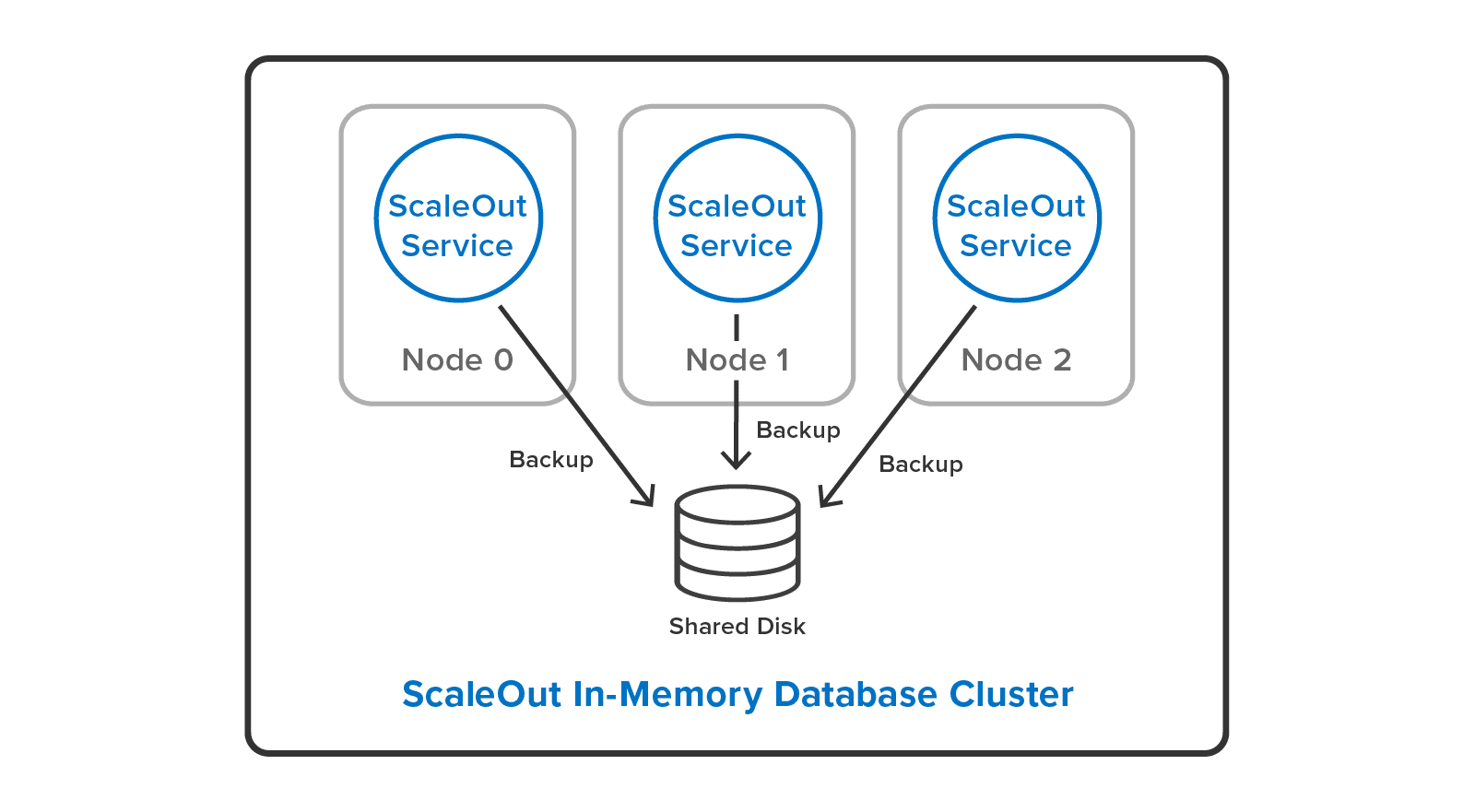
System administrators can cut down their workload by restoring backup files to a different cluster configuration than they used to make the backup. For example, it’s possible to restore a backup from a three-server cluster to a two-server cluster with a different hashslot mapping:
There’s a lot more in the new ScaleOut In-Memory Database than there’s room to discuss in depth here. For example, ScaleOut’s cluster stalls Redis command execution automatically when it moves hashslots between nodes for load-balancing, or when it performs recovery. This means clients always have a consistent view of the cluster. Also, the cluster stores Redis objects in their own ScaleOut namespace side-by-side with objects that ScaleOut’s native APIs manage. This lets users access the full power of ScaleOut’s in-memory computing features, including cluster-wide, data-parallel operations and stream processing with digital twins.
Summing Up
ScaleOut In-Memory Database makes scalable processing more convenient, reliable, and cost-effective for enterprise Redis users than ever before. By automating Redis cluster management, improving data reliability, and adding multi-threaded command execution, this product can significantly drive down the total cost of ownership for Redis deployments, even in comparison to commercial Redis alternatives. We invite you to check it out and see how it performs for you. We’d love to hear your feedback.
*Redis is a registered trademark of Redis Ltd. and the Redis box logo is a mark of Redis Ltd. Any rights therein are reserved to Redis Ltd. Any use by ScaleOut Software is for referential purposes only and does not indicate any sponsorship, endorsement or affiliation between Redis and ScaleOut Software.
The post Announcing ScaleOut In-Memory Database: Automated Clustering for Redis Users appeared first on ScaleOut Software.
]]>