The post Preventing Train Derailments Using Digital Twins appeared first on ScaleOut Software.
]]>
Using Digital Twins to Track and Simulate Large Systems
For decades, digital twins have played a crucial role in the field of product lifecycle management (PLM), where they assist in the design and testing of many types of devices, from valves to jet engines. ScaleOut Software has pioneered the use of digital twin technology combined with in-memory computing to track the behavior of live systems with many components – such as vehicle fleets, IoT devices, and even people – to monitor status in real time and boost situational awareness for operational managers.
Now, both data analysts and system managers can also harness the power of digital twins to simulate the behaviors of complex systems with thousands of interacting entities. Digital twin simulations can provide invaluable information about complex interactions that are otherwise difficult to study. They can explore scenarios often found in live systems, informing decisions and helping to identify potential issues in the planning phase. They also empower professionals to validate real-time analytics prior to deployment and to make predictions that help manage live systems.
A Case Study: Rail Transportation Safety
Consider an important use case in transportation safety for the U.S. freight railway system. The U.S moves more than 1.6 billion tons of freight over 140,000 miles of track each year. In 2022, there were 1,164 train derailments that caused damage measured in the millions of dollars and cost multiple lives. For example, in February 2023, fifty freight cars derailed in East Palestine, Ohio in a widely publicized accident. How can digital twins help prevent similar emergencies?
Currently, track-side sensors detect mechanical issues that can cause derailments, such as severely overheated wheel bearings, and radio train engineers often too late to prevent an accident. In the Ohio event, the NTSB preliminary report described increasing temperatures reported by three rail-side “hot box” detectors before the accident occurred. The U.S. railway network places these detectors every few miles across the country:

Example of a hot box detector (BBT609 – Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=25975512)
Hot box detectors capture the data needed to track increasing wheel bearing temperatures and predict impending derailments. However, safety systems need to harness this data more effectively to prevent these incidents. Digital twins can help.
Real-time analytics using digital twins can combine temperature information from multiple hot boxes to detect anomalies and take action faster, before small problems escalate into derailments. Cloud-hosted analytics can simultaneously track the entire rail network’s rolling stock using a scalable, in-memory computing platform, such as the ScaleOut Digital Twin Streaming Service , to host digital twins. They can continuously analyze patterns of temperature changes for each car’s wheel bearings, combine this with known information about the rail car, such as its maintenance history, and then assess the likelihood of failure and alert personnel within milliseconds. This use of contextual information also helps prevent false-positive alerts that create costly delays.
, to host digital twins. They can continuously analyze patterns of temperature changes for each car’s wheel bearings, combine this with known information about the rail car, such as its maintenance history, and then assess the likelihood of failure and alert personnel within milliseconds. This use of contextual information also helps prevent false-positive alerts that create costly delays.
Using Digital Twin Simulations to Design and Test Real-Time Analytics
To help railway engineers develop and test new predictive analytics software, large-scale simulations can model the flow of information from the hundreds of thousands of freight cars that cross the U.S. each day, as well as the thousands of detectors placed along the tracks. These simulations can statistically simulate emerging wheel bearing issues to test how well real-time analytics software can detect impending failures before an accident occurs. Digital twins serve double duty here; they implement real-time analytics, and they model wheel bearing failures.
As a proof of concept, ScaleOut Software created a simulation of the U.S. freight rail system to evaluate how well digital twins can track wheel bearing temperatures from multiple hot box detectors and alert engineers to avoid derailments. The simulation runs as a discrete event simulation with digital twins exchanging messages in simulated time to model interactions.
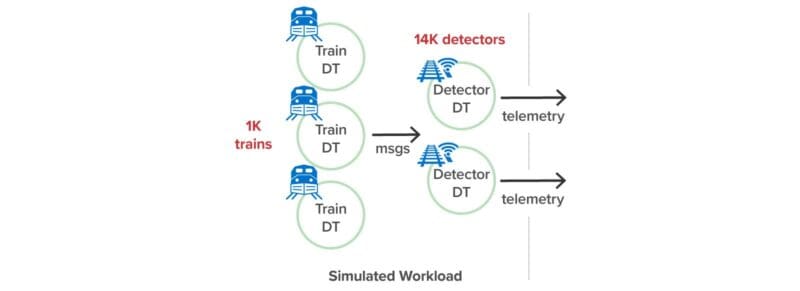
Workload Generator
This workload generator creates 500-1000 simulated trains, each with 100 freight cars and 8 wheel bearings per car. The simulated trains travel on a hypothetical rail map that crisscrosses a hypothetical U.S. rail map with 107 routes between major U.S. cities:
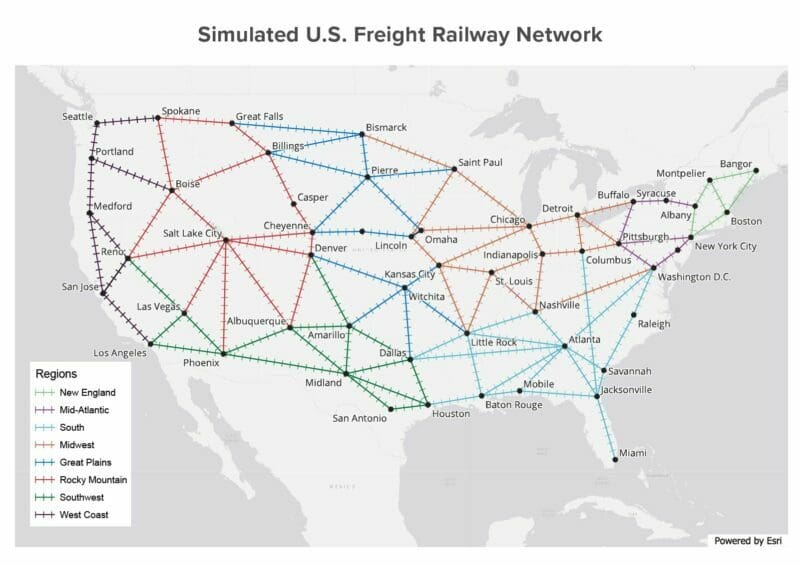
The simulated rail network places 3,800 hot box detectors approximately every 10 miles along the tracks. Each detector’s job is to report the wheel bearing temperatures for every freight car as a train passes it along the route, just as a real hot box detector would.
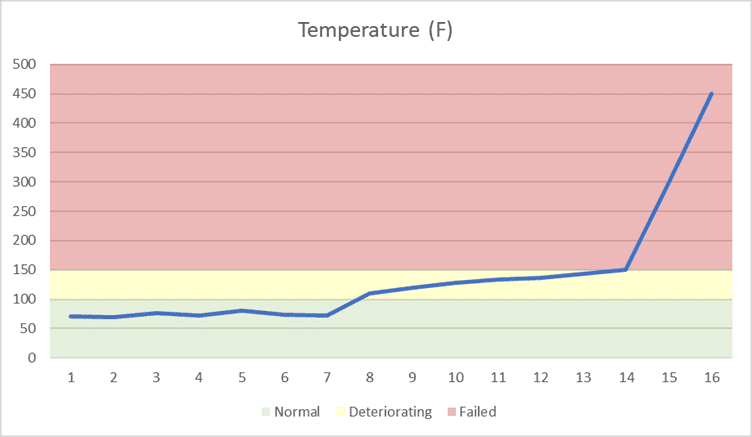
The simulation uses a separate digital twin model to implement trains and hot box detectors. (Each digital twin model has its own properties and algorithms.) A simulated train keeps track of its route, current position, speed, and freight cars. It also implements a probabilistic model of wheel bearing failures that cause a wheel bearing to enter a deteriorating state with a probability of 1:1M and then increase its temperature over time. As it passes a simulated detector, each train reports the temperature of all wheel bearings to the detector. After a deteriorating wheel bearing passes ten detectors, it increases to a 1:4 probability of entering a failed state with a rapid temperature rise. Once a bearing reaches 500 degrees Fahrenheit, the model considers it to have experienced a catastrophic failure, which corresponds to a fire or derailment.
Here is an example of a wheel bearing’s temperature profile as it passes detectors along the rails:
As simulated trains pass hot box detectors and report their wheel bearing temperatures, the detectors send a message to their corresponding real-time digital twins, which capture and analyze this telemetry.
The following diagram shows the simulation’s workload generator made up of digital twins:
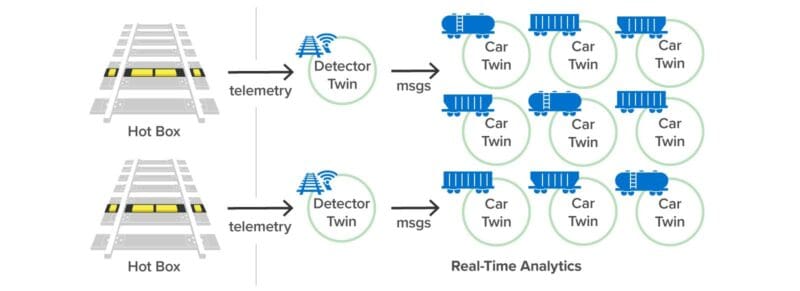
Real-Time Analytics
Digital twins also implement real-time analytics code for detecting wheel bearing failures. Once deployed in a data center for production use, they continuously track telemetry from real hot box detectors to look for possible wheel bearing failures and alert train engineers. In an actual deployment, existing hot box detectors would send messages over the cellular phone system to a cloud-based analytics service instead of just making radio broadcasts to nearby train personnel.
The analytics code uses two digital twin models, one for hot box detectors and another for individual train cars. The hot box detector twins receive telemetry messages from corresponding physical hot boxes along the tracks. Digital twins of train cars track telemetry and other relevant information about all the wheel bearings on each car. They build a picture over time of trends in wheel bearing temperatures reported by multiple detectors. They also can combine a temperature history with other contextual information, such as the type of wheel bearing and its service history, to best decide when a failure might be imminent.
In the simulation, train car digital twins just keep temperature histories for all wheel bearings and look for an upward trend over time. If a digital twin detects a potentially dangerous trend, it sends a message back to the simulated train, instructing it to stop.
To run the simulation, the workload generator sends messages to the real-time analytics: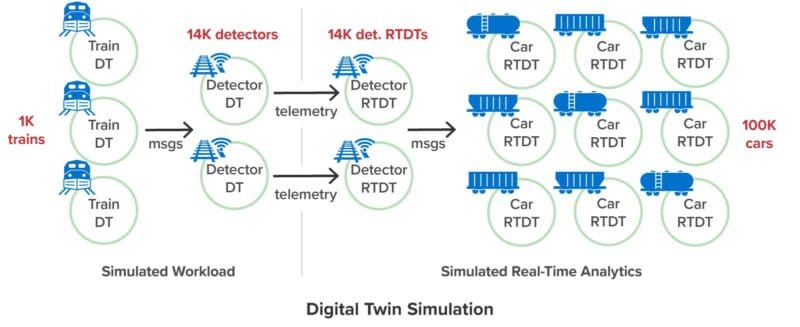
The same analytics twins can receive telemetry from actual hot box detectors after deployment:
Simulation Results
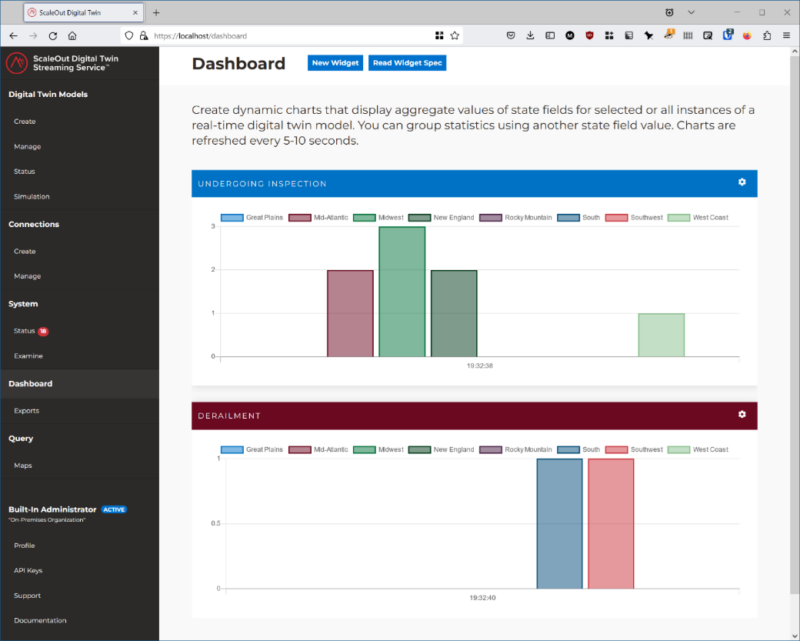
The simulation divides the U.S. rail network into regions. To check that trend analysis is working, we disable it in the south and southwest and compare it to other regions. The simulation shows that trend analysis catches all deteriorating bearings before they fail and cause derailments. Derailments only occur on routes not performing trend analysis.
The ScaleOut Digital Twin Streaming Service provides tools to visualize these results. The following dashboard widgets track the number of alerted trains by region that are undergoing inspection (because trend analysis detects an issue) along with the number of derailed trains. Note that derailments only occur in the regions with trend analysis disabled:
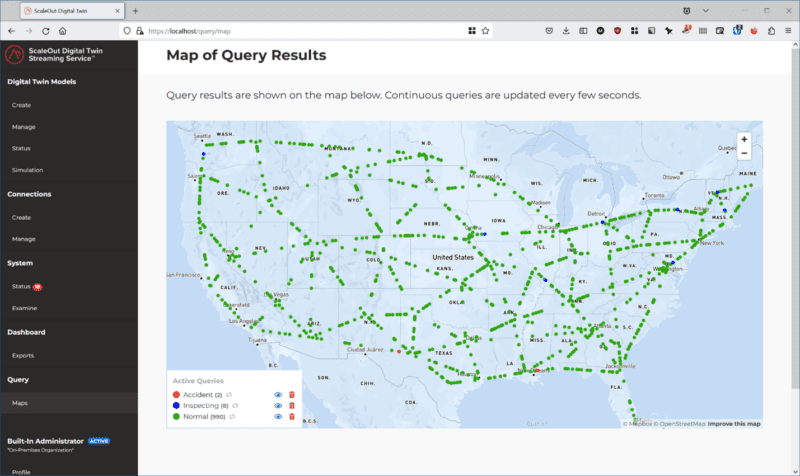
The following geospatial map of a continuous query shows the trains which are running normally in green, undergoing inspection in blue, and derailed in red. This map confirms that all derailed trains are located in the south and southwest regions and shows trains undergoing inspection in other regions:
Summing Up
The U.S. freight railways provide the backbone of the country’s freight transport system and must run with minimum disruptions. New technology like digital twins can take advantage of existing infrastructure to provide continuous monitoring that is missing today. Using scalable in-memory computing, digital twins can capture live telemetry throughout the rail system, analyze it in context, and create immediate alerts when needed. They can also implement simulations to model these issues and help planners evaluate real-time analytics software.
Beyond just watching wheel bearings, digital twins can track other areas of the rail system, such as rail intersections and switches, to further boost safety. With this technology, digital twins can help build next-generation safety systems to eliminate dangerous and costly derailments.
The post Preventing Train Derailments Using Digital Twins appeared first on ScaleOut Software.
]]>The post Simulate at Scale with Digital Twins appeared first on ScaleOut Software.
]]>
Digital Twins Can Implement Both Streaming Analytics and Simulations
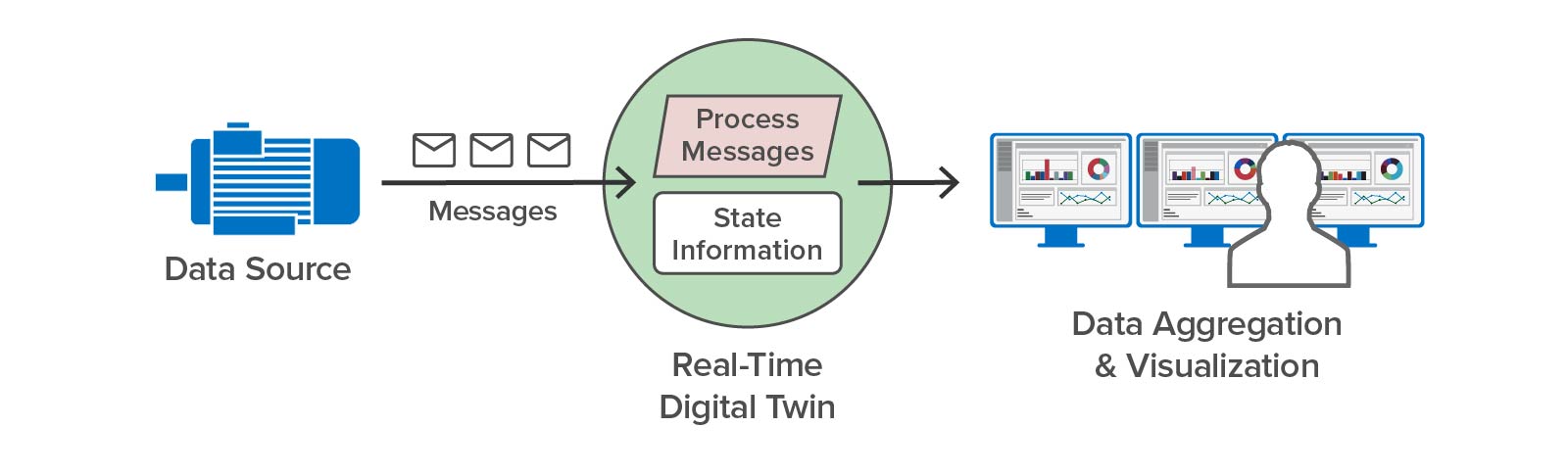
With the ScaleOut Digital Twin Streaming Service , the digital twin software model has proven its versatility well beyond its roots in product lifecycle management (PLM). This cloud-based service uses digital twins to implement streaming analytics and add important contextual information not possible with other stream-processing architectures. Because each digital twin can hold key information about an individual data source, it can enrich the analysis of incoming telemetry and extracts important, actionable insights without delay. Hosting digital twins on a scalable, in-memory computing platform enables the simultaneous tracking of thousands — or even millions — of data sources.
, the digital twin software model has proven its versatility well beyond its roots in product lifecycle management (PLM). This cloud-based service uses digital twins to implement streaming analytics and add important contextual information not possible with other stream-processing architectures. Because each digital twin can hold key information about an individual data source, it can enrich the analysis of incoming telemetry and extracts important, actionable insights without delay. Hosting digital twins on a scalable, in-memory computing platform enables the simultaneous tracking of thousands — or even millions — of data sources.
Owing to the digital twin’s object-oriented design, many diverse applications can take advantage of its powerful but easy-to-use software architecture. For example, telematics applications use digital twins to track telemetry from every vehicle in a fleet and immediately identify issues, such as lost or erratic drivers or emerging mechanical problems. Airlines can use digital twins to track the progress of passengers throughout an itinerary and respond to delays and cancellations with proactive remedies that smooth operations and reduce stress. Other applications abound, including health informatics, financial services, logistics, cybersecurity, IoT, smart cities, and crime prevention.
Here’s an example of a telematics application that tracks a large fleet of vehicles. Each vehicle has a corresponding digital twin analyzing telemetry from the vehicle in real time:
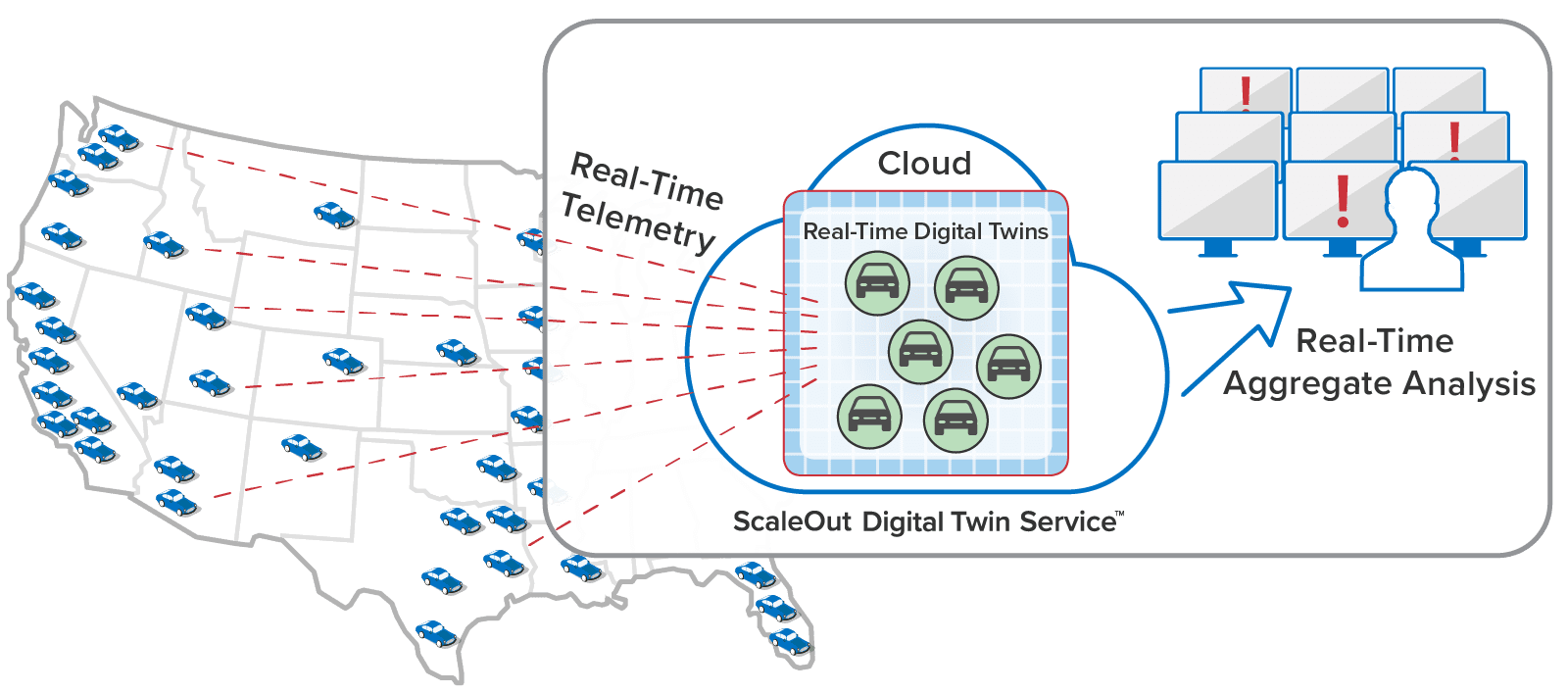
Applications like these need to simultaneously track the dynamic behavior of numerous data sources, such as IoT devices, to identify issues (or opportunities) as quickly as possible and give systems managers the best possible situational awareness. To either validate streaming analytics code for a complex physical system or model its behavior, it is useful to simulate the devices and the telemetry that they generate. The ScaleOut Digital Twin Streaming Service now enables digital twins to simplify both tasks.
Use Digital Twins to Simulate a Workload for Streaming Analytics
Digital twins can implement a workload generator that generates telemetry used in validating streaming analytics code. Each digital twin models the behavior of a physical data source, such as a vehicle in fleet, and the messages it sends and receives. When running in simulation, thousands of digital twins can then generate realistic telemetry for all data sources and feed streaming analytics, such as a telematics application, designed to track and analyze its behavior. In fact, the streaming service enables digital twins to implement both the workload generator and the streaming analytics. Once the analytics code has been validated in this manner, developers can then deploy it to track a live system.
Here’s an example of using a digital twin to simulate the operations of a pump and the telemetry (such as the pump’s temperature and RPM) that it generates. Running in simulation, this simulated pump sends telemetry messages to a corresponding real-time digital twin that analyzes the telemetry to predict impending issues:
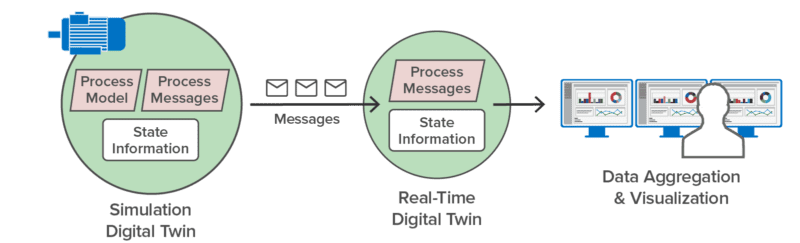
Once the simulation has validated the analytics, the real-time digital twin can be deployed to analyze telemetry from an actual pump:
This example illustrates how digital twins can both simulate devices and provide streaming analytics for a live system.
Using digital twins to build a workload generator enables investigation of a wide range of scenarios that might be encountered in typical, real-world use. Developers can implement parameterizable, stateful models of physical data sources and then vary these parameters in simulation to evaluate the ability of streaming analytics to analyze and respond in various situations. For example, digital twins could simulate perimeter devices detecting security intrusions in a large infrastructure to help evaluate how well streaming analytics can identify and classify threats. In addition, the streaming service can capture and record live telemetry and later replay it in simulation.
Use Digital Twins to Simulate a Large System with Many Entities
In addition to using digital twins for analyzing telemetry, the ScaleOut Digital Twin Streaming Service enables digital twins to implement time-driven simulations that model large groups of interacting physical entities. Digital twins can model individual entities within a large system, such as airline passengers, aircraft, airport gates, and air traffic sectors in a comprehensive airline model. These digital twins maintain state information about the physical entities they represent, and they can run code at each time step in the simulation model’s execution to update digital twin state over time. These digital twins also can exchange messages that model interactions.
For example, an airline tracking system can use simulation to model numerous types of weather delays and system outages (such as ground stops) to see how their system manages passenger needs. As the simulation model evolves over time, simulated aircraft can model flight delays and send messages to simulated passengers that react by updating their itineraries. Here is a depiction of an airline tracking simulation:
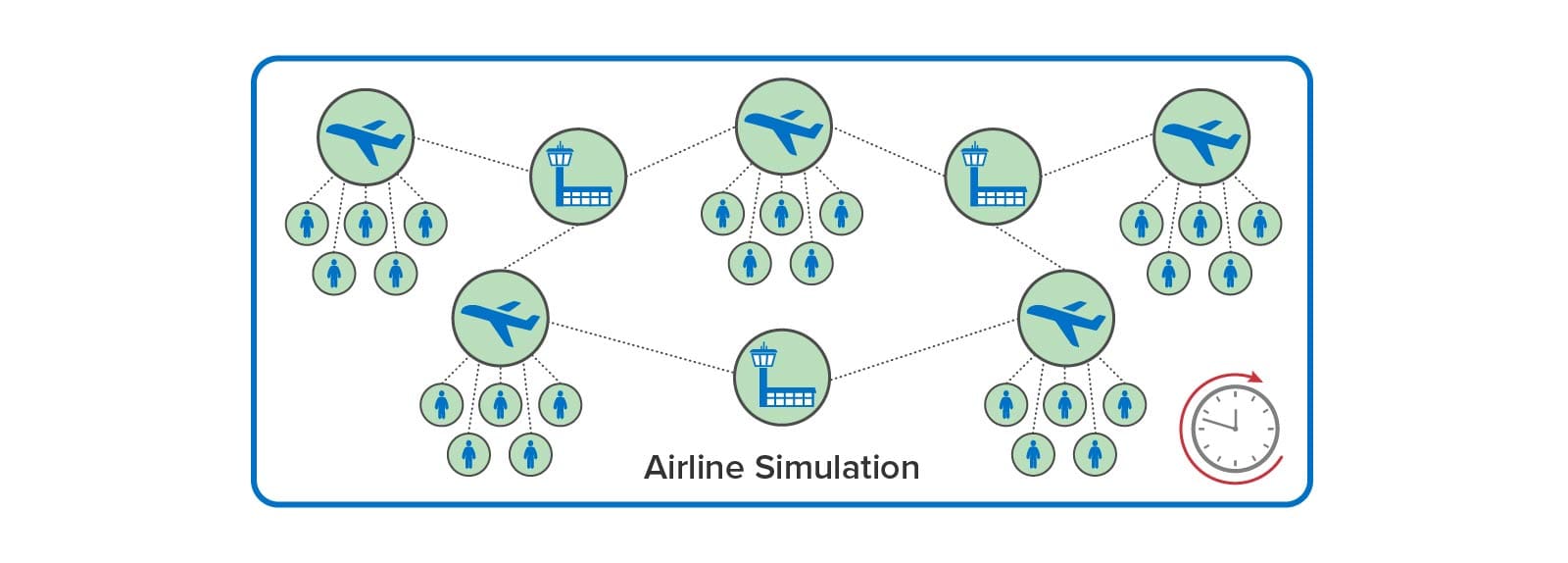
In contrast to the use of digital twins for PLM, which typically embody a complex design within a single digital twin model, the ScaleOut Digital Twin Streaming Service enables large numbers of physical entities and their interactions to be simulated. By doing this, simulations can model intricate behaviors that evolve over time and reveal important insights during system design and optimization. They also can be fed live data and run faster than real time as a tool for making predictions that assist decision-making by managers (such as airline dispatchers).
Scalable, In-Memory Computing Makes It Possible
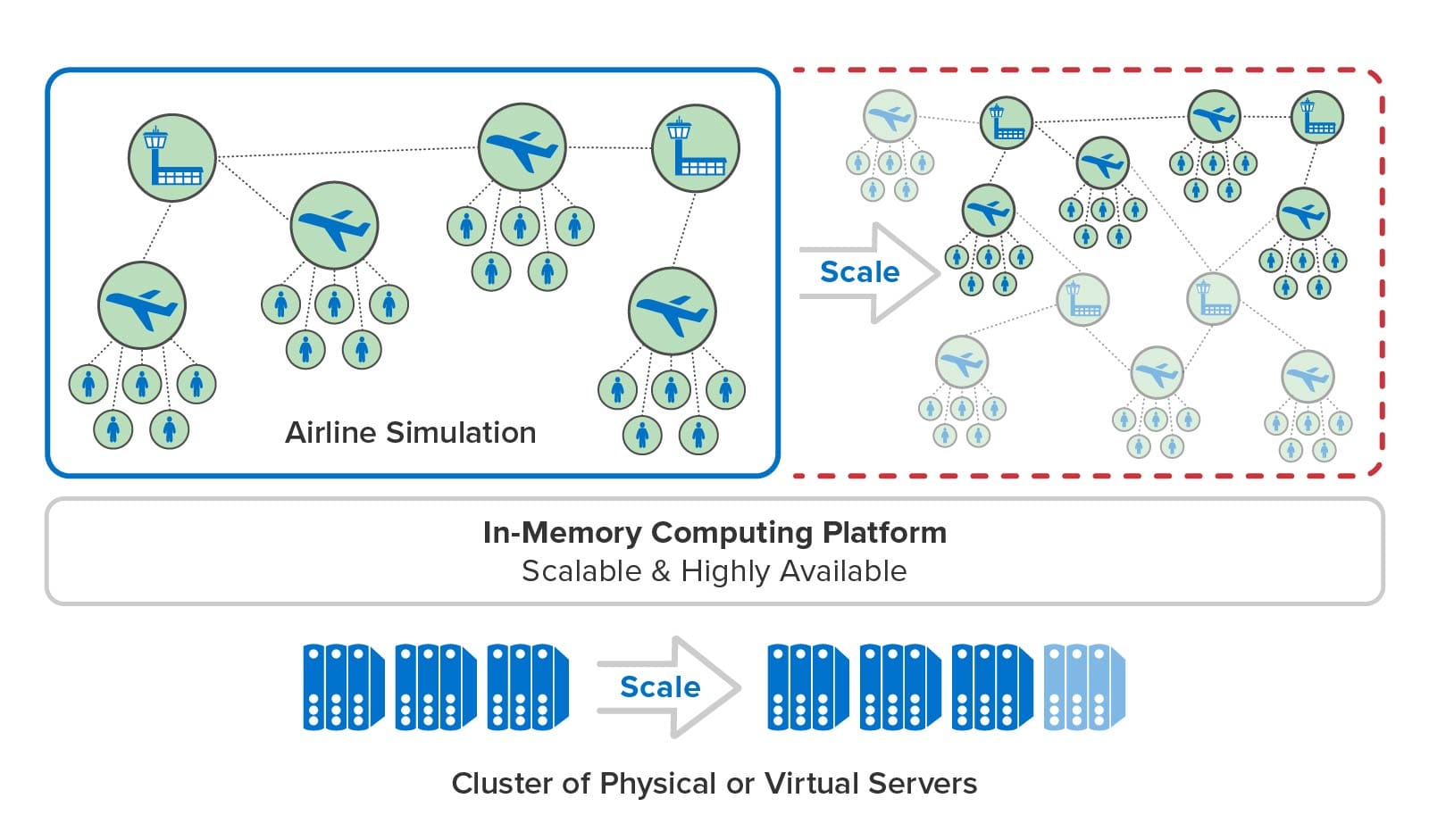
Digital twins offer a compelling software architecture for implementing time-driven simulations with thousands of entities. In a typical implementation, developers create multiple digital twin models to describe the state information and simulation code representing various physical entities, such as trucks, cargo, and warehouses in a telematics simulation. They create instances of these digital twin models (simply called digital twins) to implement all of the entities being simulated, and the streaming service runs their code at each time step being simulated. During each time step, digital twins can exchange messages that represent simulated interactions between physical entities.
The ScaleOut Digital Twin Streaming Service uses scalable, in-memory computing technology to provide the speed and memory capacity needed to run large simulations with many entities. It stores digital twins in memory and automatically distributes them across a cluster of servers that hosts a simulation. At each time step, each server runs the simulation code for a subset of the digital twins and determines the next time step that the simulation needs to run. The streaming service orchestrates the simulation’s progress on the cluster and advances simulation time at a rate selected by the user.
In this manner, the streaming service can harness as many servers as it needs to host a large simulation and run it with maximum throughput. As illustrated below, the service’s in-memory computing platform can add new servers while a simulation is running, and it can transparently handle server outages should they occur. Users need only focus on building digital twin models and deploying them to the streaming service.
The Next Generation of Simulation with Digital Twins
Digital twins have historically been employed as a tool for simulating increasingly detailed behavior of a complex physical entity, like a jet engine. The ScaleOut Digital Twin Streaming Service takes digital twins in a new direction: simulation of large systems. Its highly scalable, in-memory computing architecture enables it to easily simulate many thousands of entities and their interactions. This provides a powerful new tool for extracting insights about complex systems that today’s managers must operate at peak efficiency. Its analytics and predictive capabilities promise to offer a high return on investment in many industries.
The post Simulate at Scale with Digital Twins appeared first on ScaleOut Software.
]]>The post New Digital Twin Features for Real-World Applications appeared first on ScaleOut Software.
]]>
Using Digital Twins for Streaming Analytics
In the two years since we initially released the ScaleOut Digital Twin Streaming Service , we have applied the digital twin model to numerous use cases, including security alerting, telematics, contact tracing, logistics, device tracking, industrial sensor monitoring, cloned license plate detection, and airline system tracking. Constructing applications for these use cases has demonstrated the power of the digital twin model in creating streaming analytics that track large numbers of data sources.
, we have applied the digital twin model to numerous use cases, including security alerting, telematics, contact tracing, logistics, device tracking, industrial sensor monitoring, cloned license plate detection, and airline system tracking. Constructing applications for these use cases has demonstrated the power of the digital twin model in creating streaming analytics that track large numbers of data sources.
The process of building digital twin applications allowed us to surface both the strengths and shortcomings of our APIs. This has led to a series of new features which enhance the core platform. For example, we created a rules engine for implementing the logic within a digital twin so that new models can be created without the need for programming expertise. We then added machine learning to digital twin models using Microsoft’s ML.NET library. This enables digital twins to look for patterns in telemetry that are difficult to define with code. More recently, we integrated our digital twin model with Microsoft’s Azure Digital Twins to accelerate real-time processing using our in-memory computing technology while providing new visualization and persistence capabilities for digital twins.
With the newly announced version 2, we are adding important new capabilities for real-time analytics to our digital twin APIs. Let’s take a look at some of these new features.
New Support for .NET 6
Version 2 expands the target platforms for C#-based digital twin models by supporting .NET 6. With our goal to make the ScaleOut Digital Twin Streaming Service’s feature set and visualization tools uniformly available in the cloud and on-premises, we recognized that we needed to move beyond support for .NET Framework, which can only be deployed on Windows. By adding .NET 6, we can take advantage of its portability across both Windows and Linux. Now C#, Java, JavaScript, and rules-based digital twin models can be deployed on all platforms:
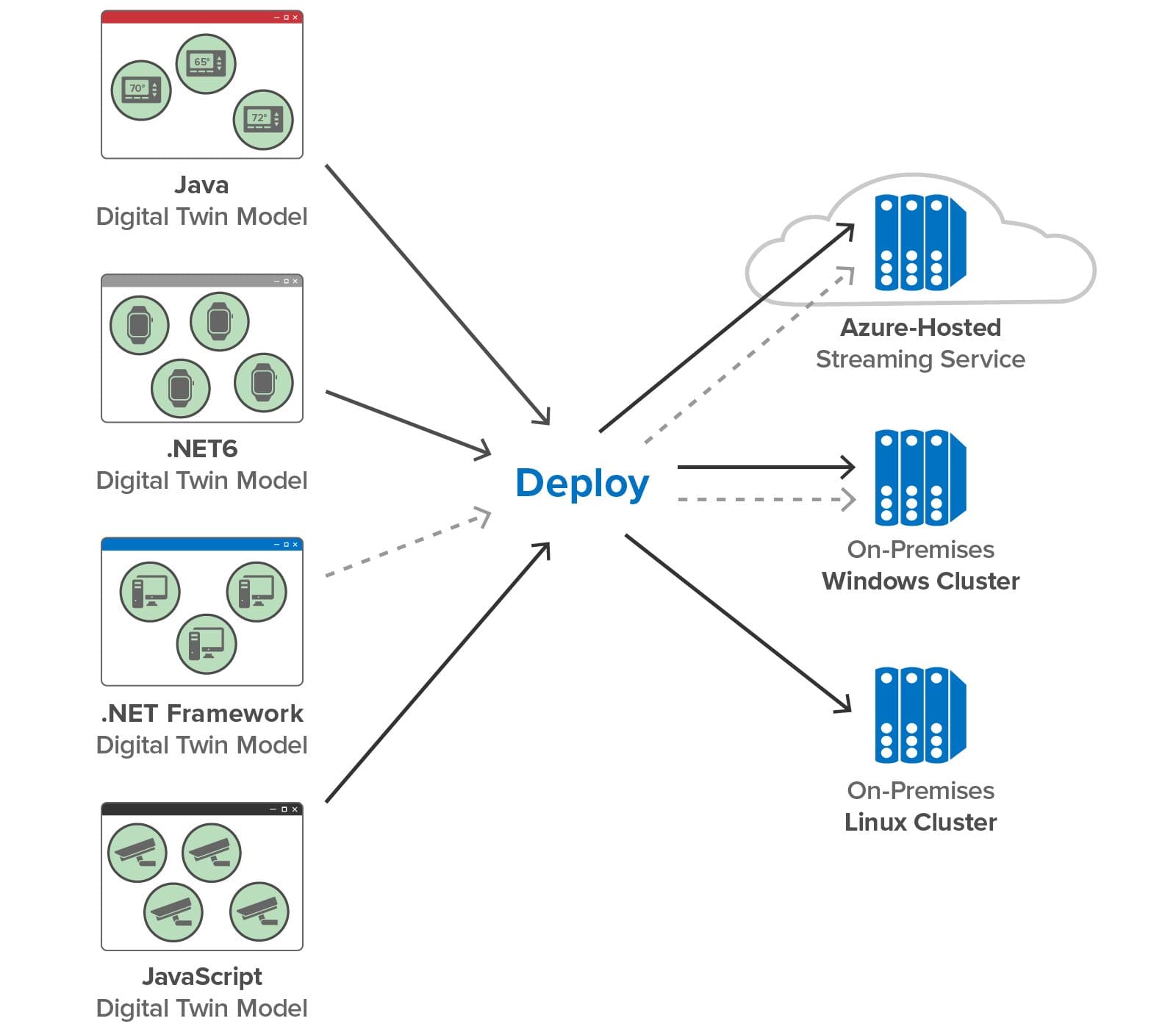
(As illustrated with the dotted lines above, we continue to support .NET Framework on Windows and in the Azure cloud.)
To take maximum advantage of .NET 6, we also re-implemented our Azure cloud service and key portions of the back-end infrastructure in .NET 6. This provides better performance and flexibility for future upgrades.
Digital Twin Timers
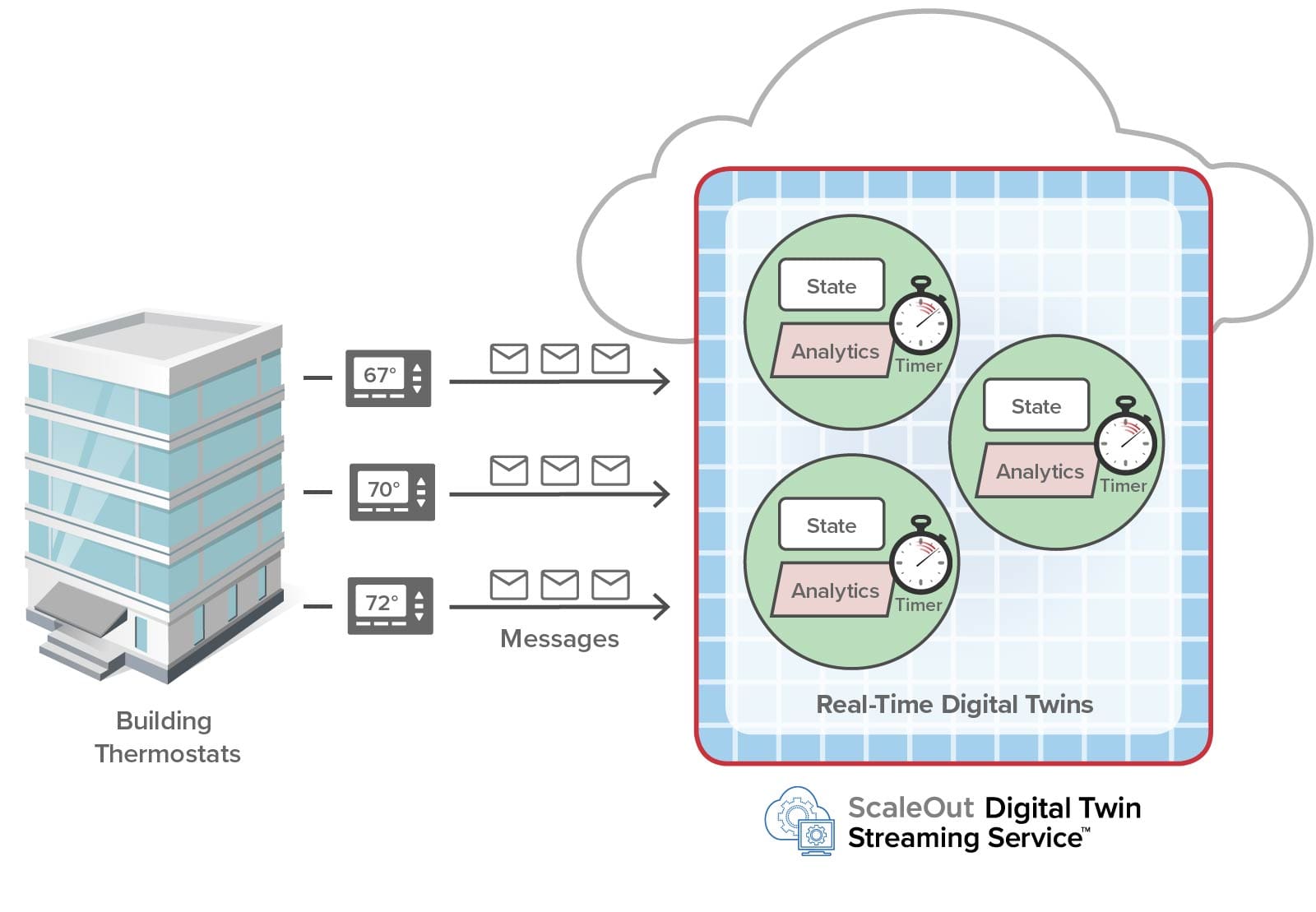
Using our APIs, digital twins can run analytics code to process incoming messages from their corresponding data sources. In developing a proof-of-concept application for an industrial safety application, we learned that they also need to be able to create timers and run code when the timers expire. This enables digital twins to detect when their data sources fail or become erratic in sending messages.
For example, consider a digital application that tracks periodic telemetry from a collection of building thermostats. Each digital twin looks for abnormal temperature excursions that indicate the need to alert personnel. In addition, a digital twin must determine if its thermostat has failed and is no longer sending periodic temperature readings. By setting a timer and restarting it after each message is received, the digital twin can signal an alert if excessive time elapses between incoming messages:
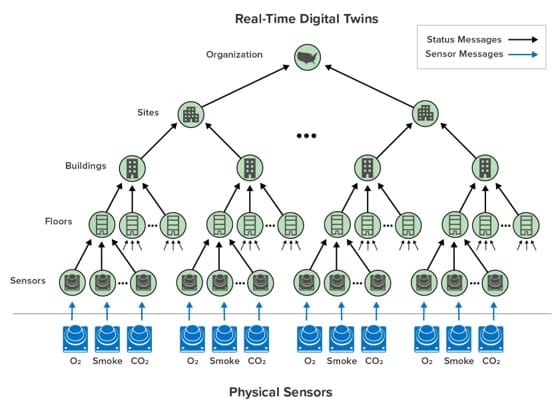
In the actual industrial safety application we built, buildings throughout a site had numerous smoke and gas sensors. Digital twins for the sensors incorporated timers to detect failed sensors. As shown below, they periodically forwarded their status to a hierarchy of digital twins arranged as shown below from the lowest level upwards. The digital twins represented floors within buildings, buildings within a site, sites within the organization, and the overall organization itself. At each level, status information was aggregated to gives personnel immediate information about where problems were occurring. The role of timers was critical in maintaining a complete picture of the organization’s status.
Aggregate Initialization
When we first implemented our digital twin platform, we designed it to automatically create a digital twin instance when the first message from an unknown data source arrives. (The platform determines which type of digital twin to create from the message’s contents.) This technique simplifies deployment by avoiding the need to explicitly create digital twin instances. The user simply develops and deploys a digital twin model, for example, for a gas sensor, and the platform creates a digital twin for each sensor that sends a message to the platform.
In many cases, it’s useful to create digital twin instances when deploying a model instead of waiting for messages to arrive. For example, both demo applications and simulations need to explicitly create digital twins since there are no actual physical devices. Also, applications with model hierarchies (like the example above) may need to create instances to fill out the hierarchy and start reporting at deployment time.
To address these needs, version 2 lets users supply a csv file when deploying a digital twin model. This csv file lists all digital twin instances and the initial values for each instance’s properties. The platform then creates the corresponding digital twin instances and sets the initial values.
Here’s an example that shows how a csv file generated from a spreadsheet can be deployed to the streaming service via the UI to initialize five digital twin instances. Note that the spreadsheet’s first row has the names of the properties to be set:
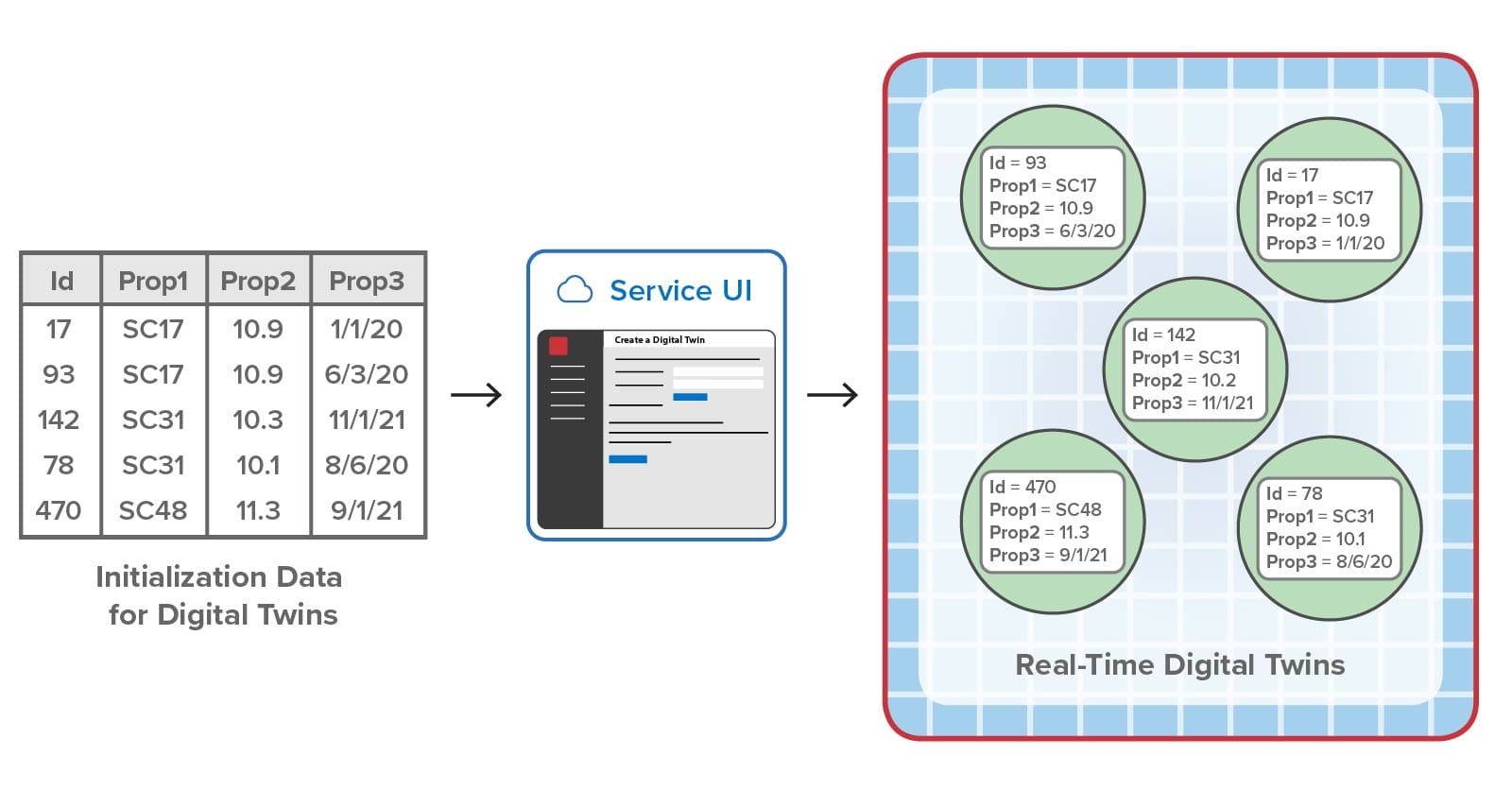
Summing Up
After more than two years of experience in building real-world applications with digital twins, we have confirmed the power of using digital twins for streaming analytics. Because digital twins bring together state information, telemetry, and application logic for each physical device, they enable deep introspection that tracks behavior and surfaces issues using a simple, highly efficient programming model. They also allow applications to focus on analytics code and defer the challenges of data visualization and throughput scaling to the streaming service.
With version 2, we have added important new capabilities to our implementation of the digital twin model and to the underlying platform. These features have been driven by emerging requirements that surfaced during application development. This matches our design philosophy of starting with a simple, coherent model and carefully enhancing it as new learnings are made.
Interestingly, our development work has consistently shown the value of using simulation to demonstrate the capabilities of the digital twin model for streaming analytics. The new features in version 2 enhance our ability to build simulations, and we expect to add more support for simulation in upcoming releases. Stay tuned.
The post New Digital Twin Features for Real-World Applications appeared first on ScaleOut Software.
]]>The post Unlocking New Capabilities for Azure Digital Twins with Real-Time Analytics appeared first on ScaleOut Software.
]]>
The Need for Real-Time Analytics with Digital Twins
In countless applications that track live systems, real-time analytics plays a key role in identifying problems (or finding opportunities) and responding fast enough to make a difference. Consider a software telematics application that tracks a nationwide fleet of trucks to ensure timely deliveries. Dispatchers receive telemetry from trucks every few seconds detailing location, speed, lateral acceleration, engine parameters, and cargo viability. In a classic needle-and-haystack scenario, dispatchers must continuously sift through telemetry from thousands of trucks to spot issues, such as lost or fatigued drivers, engines requiring maintenance, or unreliable cargo refrigeration. They must intervene quickly to keep the supply chain running smoothly. Real-time analytics can help dispatchers tackle this seemingly impossible task by automatically sifting through telemetry as it arrives, analyzing it for anomalies needing attention, and alerting dispatchers when conditions warrant.
By using a process of divide and conquer, digital twins can dramatically simplify the construction of applications that implement real-time analytics for telematics or other applications. A digital twin for each truck can track that truck’s parameters (for example, maintenance and driver history) and its dynamic state (location, speed, engine and cargo condition, etc.). The digital twin can analyze telemetry from the truck to update this state information and generate alerts when needed. It can encapsulate analytics code or use machine learning techniques to look for anomalies. Running simultaneously, thousands of digital twins can track all the trucks in a fleet to keep dispatchers informed while reducing their workload.
Applying the digital twin model to real-time analytics expands its range of uses from its traditional home in product lifecycle management and infrastructure tracking to managing time-critical, live systems with many data sources. Examples include preventive maintenance, health-device tracking, logistics, physical and cyber security, IoT for smart cities, ecommerce shopping, financial services, and many others. But how can we integrate real-time analytics with digital twins and ensure high performance combined with straightforward application development?
Message Processing with Azure Digital Twins
Microsoft’s Azure Digital Twins provides a compelling platform for creating digital twin models with a rich set of features for describing their contents, including properties, components, inheritance, and more. The Azure Digital Twins Explorer GUI tool lets users view digital twin models and instances, as well as their relationships.
Azure digital twins can host dynamic properties that track the current state of physical data sources. Users can create serverless functions using Azure Functions to ingest messages generated by data sources and delivered to digital twins via Azure IoT Hub (or other message hubs). These functions update the properties of Azure digital twins using APIs provided for this purpose. Here’s a redrawn tutorial example that shows how Azure functions can process messages from a thermostat and update both its digital twin and a parent digital twin that models the room in which the thermostat is located. Note that the first Azure function’s update triggers the Azure Event Grid to run a second function that updates the room’s property:
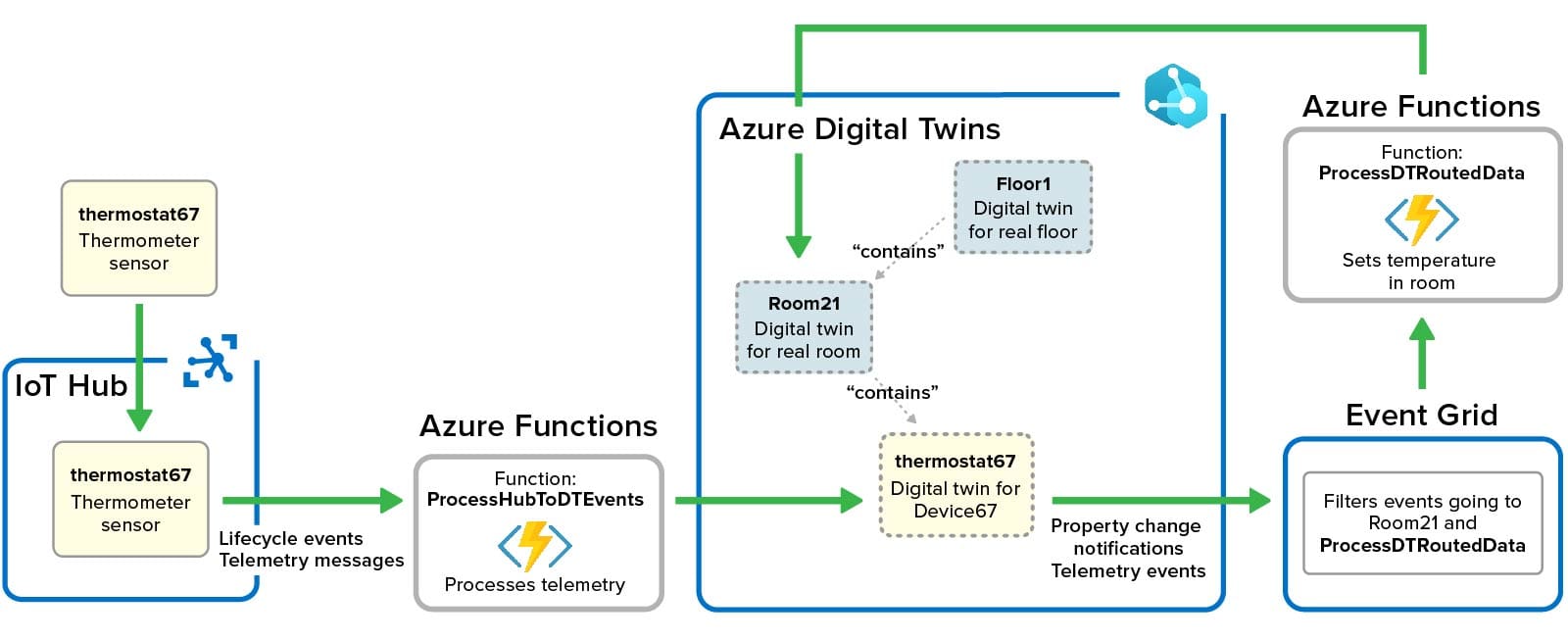
The challenge in using serverless functions to process messages and perform real-time analytics is that they add overhead and complexity. By their nature, serverless functions are stateless and must obtain their state from external services; this adds latency. In addition, they are subject to scheduling and authentication overheads on each invocation, and this adds delays that limit scalability. The use of multiple serverless functions and associated mechanisms, such as Event Grid topics and routes, also adds complexity in developing analytics code.
Adding Real-Time Analytics Using In-Memory Computing
Integrating an in-memory computing platform with the Azure Digital Twins infrastructure addresses both of the challenges. This technology runs on a cluster of virtual servers and hosts application-defined software objects in memory for fast access along with a software-based compute engine that can run application-defined methods with extremely low latency. By storing each Azure digital twin instance’s properties in memory and routing incoming messages to an in-memory method for processing, both latency and complexity can be dramatically reduced, and real-time analytics can be scaled to handle thousands or even millions of data sources.
ScaleOut Software’s newly announced Azure Digital Twins Integration does just this. It integrates the ScaleOut Digital Twin Streaming Service , an in-memory computing platform running on Microsoft Azure (or on premises), with the Azure Digital Twins service to provide real-time streaming analytics. It accelerates message processing using in-memory computing to ensure fast, scalable performance while simultaneously streamlining the programming model.
, an in-memory computing platform running on Microsoft Azure (or on premises), with the Azure Digital Twins service to provide real-time streaming analytics. It accelerates message processing using in-memory computing to ensure fast, scalable performance while simultaneously streamlining the programming model.
The ScaleOut Azure Digital Twins Integration creates a component within an Azure Digital Twin model in which it hosts “real-time” properties for each digital twin instance of the model. These properties track dynamic changes to the instance’s physical data source and provide context for real-time analytics.
To implement real-time analytics code, application developers create a message-processing method for an Azure digital twin model. This method can be written in C# or Java, using an intuitive rules-based language, or by configuring machine learning (ML) algorithms implemented by Microsoft’s ML.NET library. It makes use of each instance’s real-time properties, which it stores in a memory-based object called a real-time digital twin, and the in-memory compute engine automatically persists these properties in the Azure digital twin instance.
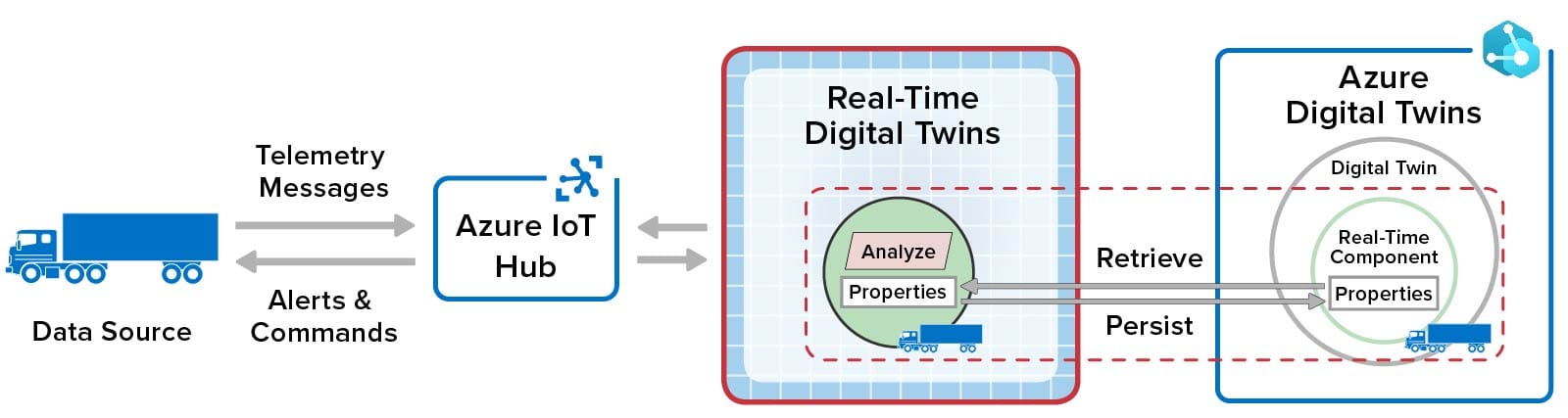
Here’s a diagram that illustrates how real-time digital twins integrate with Azure digital twins to provide real-time streaming analytics:
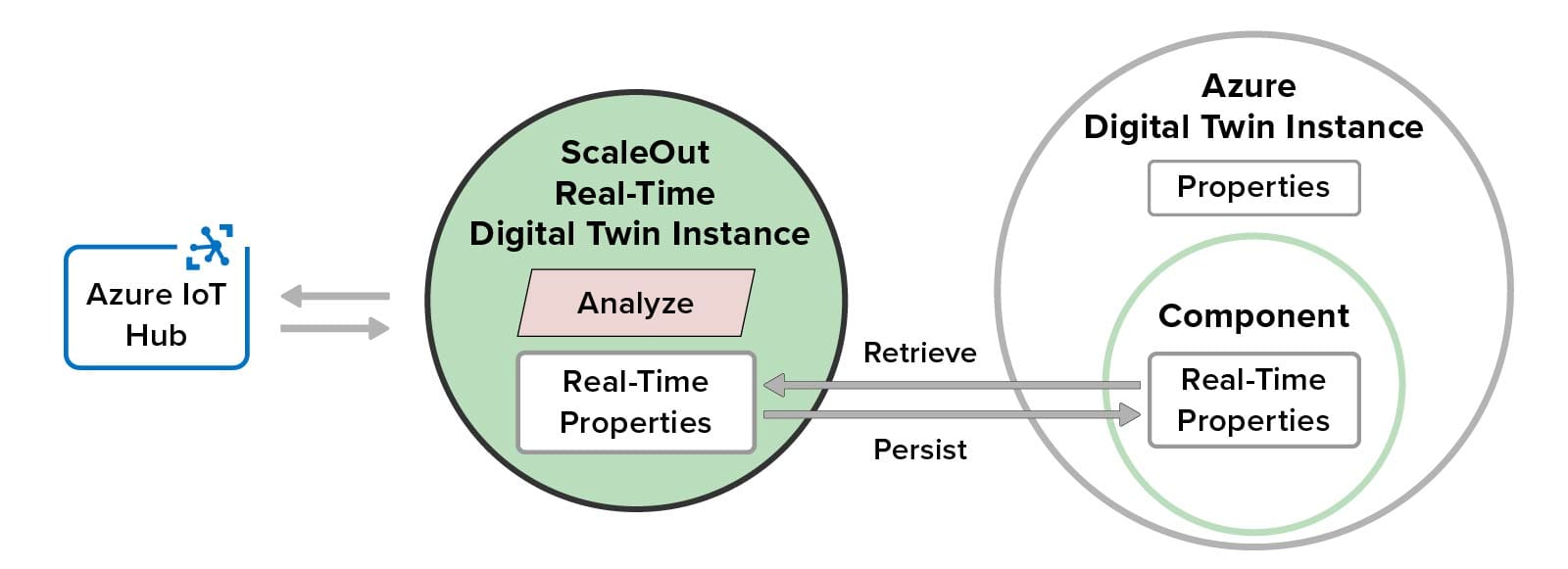
This diagram shows how each real-time digital twin instance maintains in-memory properties, which it retrieves when deployed, and automatically persists these properties in its corresponding Azure digital twin instance. The real-time digital twin connects to Azure IoT Hub or other message source to receive and then analyze incoming messages from its corresponding data source. Fast, in-memory processing provides sub-millisecond access to real-time properties and completes message processing with minimal latency. It also avoids repeated authentication delays every time a message is processed by authenticating once with the Azure Digital Twins service at startup.
All real-time analytics performed during message processing can run within a single in-memory method that has full access to the digital twin instance’s properties. This code also can access and update properties in other Azure digital twin instances. These features simplify design by avoiding the need to split functionality across multiple serverless functions and by providing a straightforward, object-oriented design framework with advanced, built-in capabilities, such as ML.
To further accelerate development, ScaleOut provides tools that automatically generate Azure digital twin model definitions for real-time properties. These model definitions can be used either to create new digital twin models or to add a real-time component to an existing model. Users just need to upload the model definitions to the Azure Digital Twins service.
Here’s how the tutorial example for the thermostat would be implemented using ScaleOut’s Azure Digital Twins Integration:
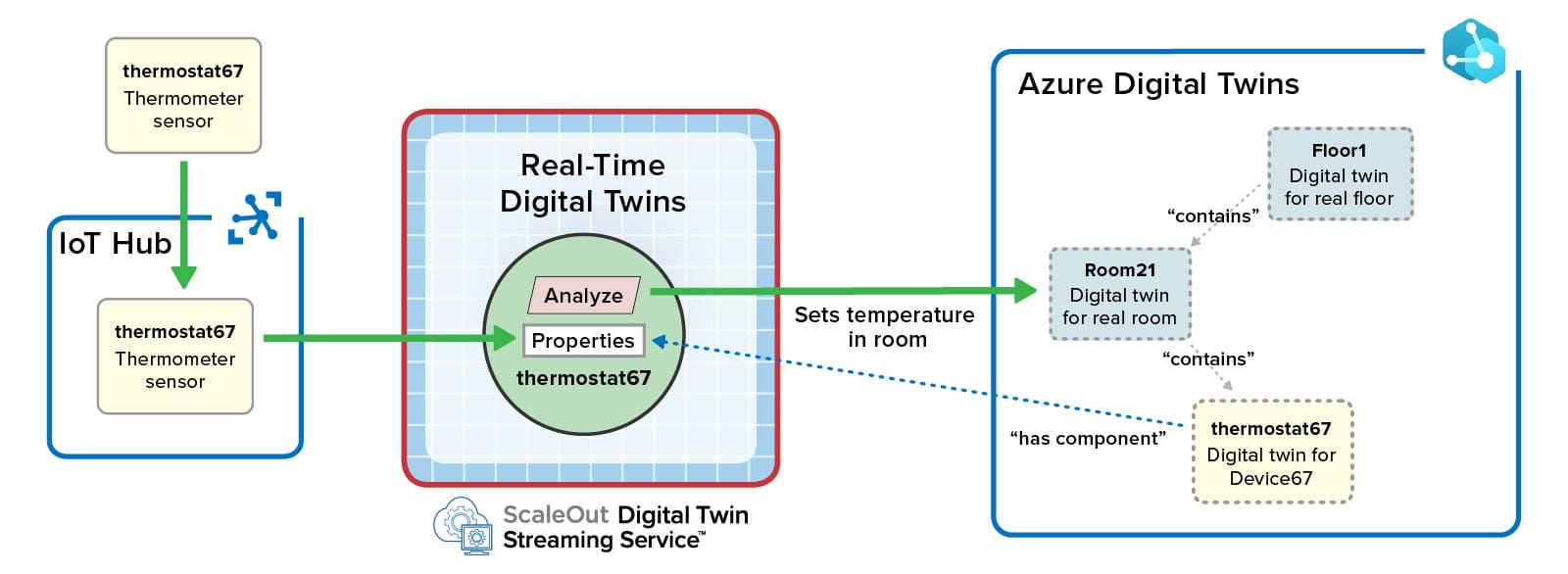 Note that the ScaleOut Digital Twins Streaming Service takes responsibility for ingesting messages from Azure IoT Hub and for invoking analytics code for the data source’s incoming messages. Multiple, pipelined connections with Azure IoT Hub ensure high throughput. Also note that the two serverless functions and use of Event Grid have been eliminated since the in-memory method handles both message processing and updates to the parent object (Room 21).
Note that the ScaleOut Digital Twins Streaming Service takes responsibility for ingesting messages from Azure IoT Hub and for invoking analytics code for the data source’s incoming messages. Multiple, pipelined connections with Azure IoT Hub ensure high throughput. Also note that the two serverless functions and use of Event Grid have been eliminated since the in-memory method handles both message processing and updates to the parent object (Room 21).
Combining the ScaleOut Digital Twin Streaming Service with Azure Digital Twins gives users the power of in-memory computing for real-time analytics while leveraging the full spectrum of Azure services and tools, as illustrated below for the thermostat example:
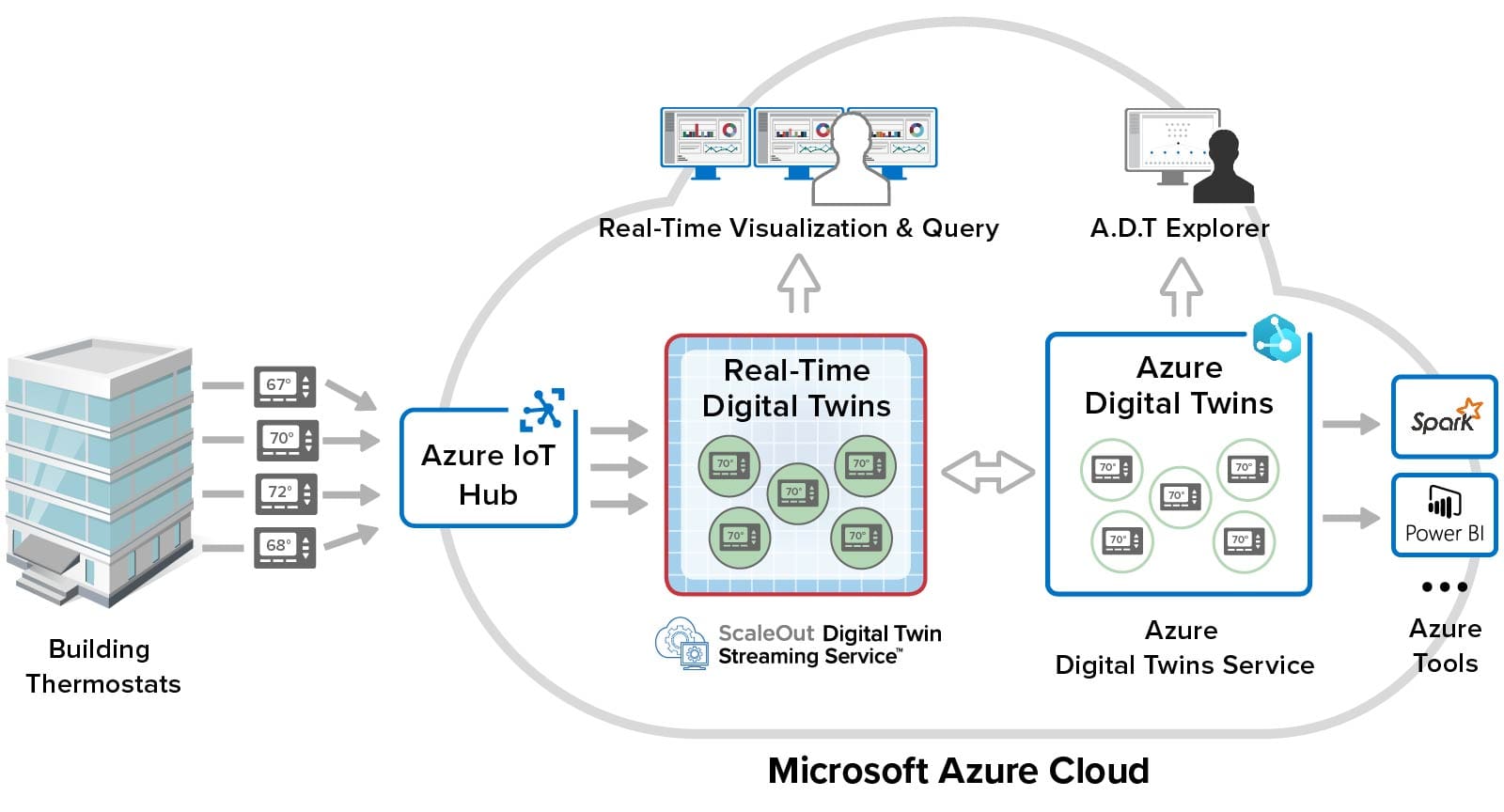
Users can view real-time properties with the Azure Digital Twins Explorer tool and track changes due to message processing. They also can take advantage of Azure’s ecosystem of big data analytics tools like Spark to perform batch processing. ScaleOut’s real-time data aggregation, continuous query, and visualization tools for real-time properties enable second-by-second tracking of live systems that boosts situational awareness for users.
Example of Real-Time Analytics with Azure Digital Twins
Incorporating real-time analytics using ScaleOut’s Azure Digital Twins Integration unlocks a wide array of applications for Azure Digital Twins. For example, here’s how the telematics software application discussed above could be implemented:
Each truck has a corresponding Azure digital twin which tracks its properties including a subset of real-time properties held in a component of each instance. When telemetry messages flow in to Azure IoT Hub, they are processed and analyzed by ScaleOut’s in-memory computing platform using a real-time digital twin that holds a truck’s real-time properties in memory for fast access and a message-processing method that analyzes telemetry changes, updates properties, and signals alerts when needed.
Real-time analytics can run ML algorithms that continuously examine telemetry, such as engine parameters, to detect anomalies and signal alerts. Digital twin analytics, combined with data aggregation and visualization powered by the in-memory platform, enable dispatchers to quickly spot emerging issues and take corrective action in a timely manner.
Summing Up
Digital twins offer a powerful means to model and visualize a population of physical devices. Adding real-time analytics to digital twins extends their reach into live, production systems that perform time-sensitive functions. By enabling managers to continuously examine telemetry from thousands or even millions of data sources and immediately identify emerging issues, they can avoid costly problems and capture elusive opportunities.
Azure Digital Twins has emerged as a compelling platform for hosting digital twin models. With the integration of in-memory computing technology using the ScaleOut Digital Twin Streaming Service, Azure Digital Twins gains the ability to analyze incoming telemetry with low latency, high scalability, and a straightforward development model. The combination of these two technologies has the potential to unlock a wide range of important new use cases for digital twins.
The post Unlocking New Capabilities for Azure Digital Twins with Real-Time Analytics appeared first on ScaleOut Software.
]]>The post The Need for Real-Time Device Tracking appeared first on ScaleOut Software.
]]>Real-Time Device Tracking with In-Memory Computing Can Fill an Important Gap in Today’s Streaming Analytics Platforms
We are increasingly surrounded by intelligent IoT devices, which have become an essential part of our lives and an integral component of business and industrial infrastructures. Smart watches report biometrics like blood pressure and heartrate; sensor hubs on long-haul trucks and delivery vehicles report telemetry about location, engine and cargo health, and driver behavior; sensors in smart cities report traffic flow and unusual sounds; card-key access devices in companies track entries and exits within businesses and factories; cyber agents probe for unusual behavior in large network infrastructures. The list goes on.
The Limitations of Today’s Streaming Analytics
How are we managing the torrent of telemetry that flows into analytics systems from these devices? Today’s streaming analytics architectures are not equipped to make sense of this rapidly changing information and react to it as it arrives. The best they can usually do in real-time using general purpose tools is to filter and look for patterns of interest. The heavy lifting is deferred to the back office. The following diagram illustrates a typical workflow. Incoming data is saved into data storage (historian database or log store) for query by operational managers who must attempt to find the highest priority issues that require their attention. This data is also periodically uploaded to a data lake for offline batch analysis that calculates key statistics and looks for big trends that can help optimize operations.
![]()
What’s missing in this picture? This architecture does not apply computing resources to track the myriad data sources sending telemetry and continuously look for issues and opportunities that need immediate responses. For example, if a health tracking device indicates that a specific person with known health condition and medications is likely to have an impending medical issue, this person needs to be alerted within seconds. If temperature-sensitive cargo in a long haul truck is about to be impacted by an erratic refrigeration system with known erratic behavior and repair history, the driver needs to be informed immediately. If a cyber network agent has observed an unusual pattern of failed login attempts, it needs to alert downstream network nodes (servers and routers) to block the kill chain in a potential attack.
A New Approach: Real-Time Device Tracking
To address these challenges and countless others like them, we need autonomous, deep introspection on incoming data as it arrives and immediate responses. The technology that can do this is called in-memory computing. What makes in-memory computing unique and powerful is its two-fold ability to host fast-changing data in memory and run analytics code within a few milliseconds after new data arrives. It can do this simultaneously for millions of devices. Unlike manual or automatic log queries, in-memory computing can continuously run analytics code on all incoming data and instantly find issues. And it can maintain contextual information about every data source (like the medical history of a device wearer or the maintenance history of a refrigeration system) and keep it immediately at hand to enhance the analysis. While offline, big data analytics can provide deep introspection, they produce answers in minutes or hours instead of milliseconds, so they can’t match the timeliness of in-memory computing on live data.
The following diagram illustrates the addition of real-time device tracking with in-memory computing to a conventional analytics system. Note that it runs alongside existing components. It adds the ability to continuously examine incoming telemetry and generate both feedback to the data sources (usually, devices) and alerts for personnel in milliseconds:
![]()
In-Memory Computing with Real-Time Digital Twins
Let’s take a closer look at today’s conventional streaming analytics architectures, which can be hosted in the cloud or on-premises. As shown in the following diagram, a typical analytics system receives messages from a message hub, such as Kafka, which buffers incoming messages from the data sources until they can be processed. Most analytics systems have event dashboards and perform rudimentary real-time processing, which may include filtering an aggregated incoming message stream and extracting patterns of interest. These real-time components then deliver messages to data storage, which can include a historian database for logging and query and a data lake for offline, batch processing using big data tools such as Spark:
![]()
Conventional streaming analytics systems run either manual queries or automated, log-based queries to identify actionable events. Since big data analyses can take minutes or hours to run, they are typically used to look for big trends, like the fuel efficiency and on-time delivery rate of a trucking fleet, instead of emerging issues that need immediate attention. These limitations create an opportunity for real-time device tracking to fill the gap.
As shown in the following diagram, an in-memory computing system performing real-time device tracking can run alongside the other components of a conventional streaming analytics solution and provide autonomous introspection of the data streams from each device. Hosted on a cluster of physical or virtual servers, it maintains memory-based state information about the history and dynamically evolving state of every data source. As messages flow in, the in-memory compute cluster examines and analyzes them separately for each data source using application-defined analytics code. This code makes use of the device’s state information to help identify emerging issues and trigger alerts or feedback to the device. In-memory computing has the speed and scalability needed to generate responses within milliseconds, and it can evaluate and report aggregate trends every few seconds.
![]()
Because in-memory computing can store contextual data and process messages separately for each data source, it can organize application code using a software-based digital twin for each device, as illustrated in the diagram above. Instead of using the digital twin concept to model the inner workings of the device, a real-time digital twin tracks the device’s evolving state coupled with its parameters and history to detect and predict issues needing immediate attention. This provides an object-oriented mechanism that simplifies the construction of real-time application code that needs to evaluate incoming messages in the context of the device’s dynamic state. For example, it enables a medical application to determine the importance of a change in heart rate for a device wearer based on the individual’s current activity, age, medications, and medical history.
Summing Up
The complex web of communicating devices that surrounds us needs intelligent, real-time device tracking to extract its full benefits. Conventional streaming analytics architectures have not kept up with the growing demands of IoT. With its combination of fast data storage, low-latency processing and ease of use, in-memory computing can fill the gap while complementing the benefits provided by historian databases and data lakes. It can add the immediate feedback that IoT applications need and boost situational awareness to a new level, finally enabling IoT to deliver on its promises.
The post The Need for Real-Time Device Tracking appeared first on ScaleOut Software.
]]>The post Adding New Capabilities for Real-Time Analytics to Azure IoT appeared first on ScaleOut Software.
]]>
The population of intelligent IoT devices is exploding, and they are generating more telemetry than ever. Whether it’s health-tracking watches, long-haul trucks, or security sensors, extracting value from these devices requires streaming analytics that can quickly make sense of the telemetry and intelligently react to handle an emerging issue or capture a new opportunity.
The Microsoft Azure IoT ecosystem offers a rich set of capabilities for processing IoT telemetry, from its arrival in the cloud through its storage in databases and data lakes. Acting as a switchboard for incoming and outgoing messages, Azure IoT Hub forms the core of these capabilities. It provides support for a range of message protocols, buffering, and scalable message distribution to downstream services. These services include:
- Azure Event Grid for routing incoming events to a variety of handlers, including serverless functions, webhooks, storage queues, and other services
- Azure IoT Central for managing devices, visualizing incoming telemetry on a dashboard, triggering alerts, and integrating with line-of-business applications
- Azure Stream Analytics for simultaneously analyzing aggregated telemetry streams using extended SQL queries to extract patterns that can be fed to workflows, including alerts, serverless functions, and data storage with offline processing
- Azure Time Series Insights for storing time-series data and then exploring, modeling, and querying it to gain insights, such as identifying anomalies and trends, with a rich set of analytics tools
- Azure Digital Twins for creating a graphical representation of the assets within an organization using the Digital Twin Definition Language, processing events, and visualizing entity graphs to display and query status
While Azure IoT offers a wide variety of services, it focuses on visualizing entities and events, extracting insights from telemetry streams with queries, and migrating events to storage for more intensive offline analysis. What’s missing is continuous, real-time introspection on the dynamic state of IoT devices to predict and immediately react to significant changes in their state. These capabilities are vitally important to extract the full potential of real-time intelligent monitoring.
For example, here are some scenarios in which stateful, real-time introspection can create important insights. Telemetry from each truck in a fleet of thousands can provide numerous parameters about the driver (such as repeated lateral accelerations at the end of a long shift) that might indicate the need for a dispatcher to intervene. A health tracking device might indicate a combination of signals (blood pressure, blood oxygen, heart rate, etc.) that indicate an emerging medical issue for an individual with a known medical history and current medications. A security sensor in a key-card access system might indicate an unusual pattern of building entries for an employee who has given notice of resignation.
In all of these examples, the event-processing system needs to be able to independently analyze events for each data source (IoT device) within milliseconds, and it needs immediate access to dynamic, contextual information about the data source that it can use to perform real-time predictive analytics. In short, what’s needed is a scalable, in-memory computing platform connected directly to Azure IoT Hub which can ingest and process event messages separately for each data source using memory-based state information maintained for that data source.
The ScaleOut Digital Twin Streaming Service provides precisely these capabilities. It does this by leveraging the digital twin concept (not to be confused with Azure Digital Twins) to create an in-memory software object for every data source that it is tracking. This object, called a real-time digital twin, holds dynamic state information about the data source and is made available to the application’s event handling code, which runs within 1-2 milliseconds whenever an incoming event is received. Application developers write event handling code in C#, Java, JavaScript, or using a rules engine; this code encapsulates application logic, such as a predictive analytics or machine learning algorithm. Once the real-time digital twin’s model (that is, its state data and event handling code) has been created, the developer can use an intuitive UI to deploy it to the streaming service and connect to Azure IoT Hub.
provides precisely these capabilities. It does this by leveraging the digital twin concept (not to be confused with Azure Digital Twins) to create an in-memory software object for every data source that it is tracking. This object, called a real-time digital twin, holds dynamic state information about the data source and is made available to the application’s event handling code, which runs within 1-2 milliseconds whenever an incoming event is received. Application developers write event handling code in C#, Java, JavaScript, or using a rules engine; this code encapsulates application logic, such as a predictive analytics or machine learning algorithm. Once the real-time digital twin’s model (that is, its state data and event handling code) has been created, the developer can use an intuitive UI to deploy it to the streaming service and connect to Azure IoT Hub.
As shown in the following diagram, ScaleOut’s streaming service connects to Azure IoT Hub, runs alongside other Azure IoT services, and provides unique capabilities that enhance the overall Azure IoT ecosystem:
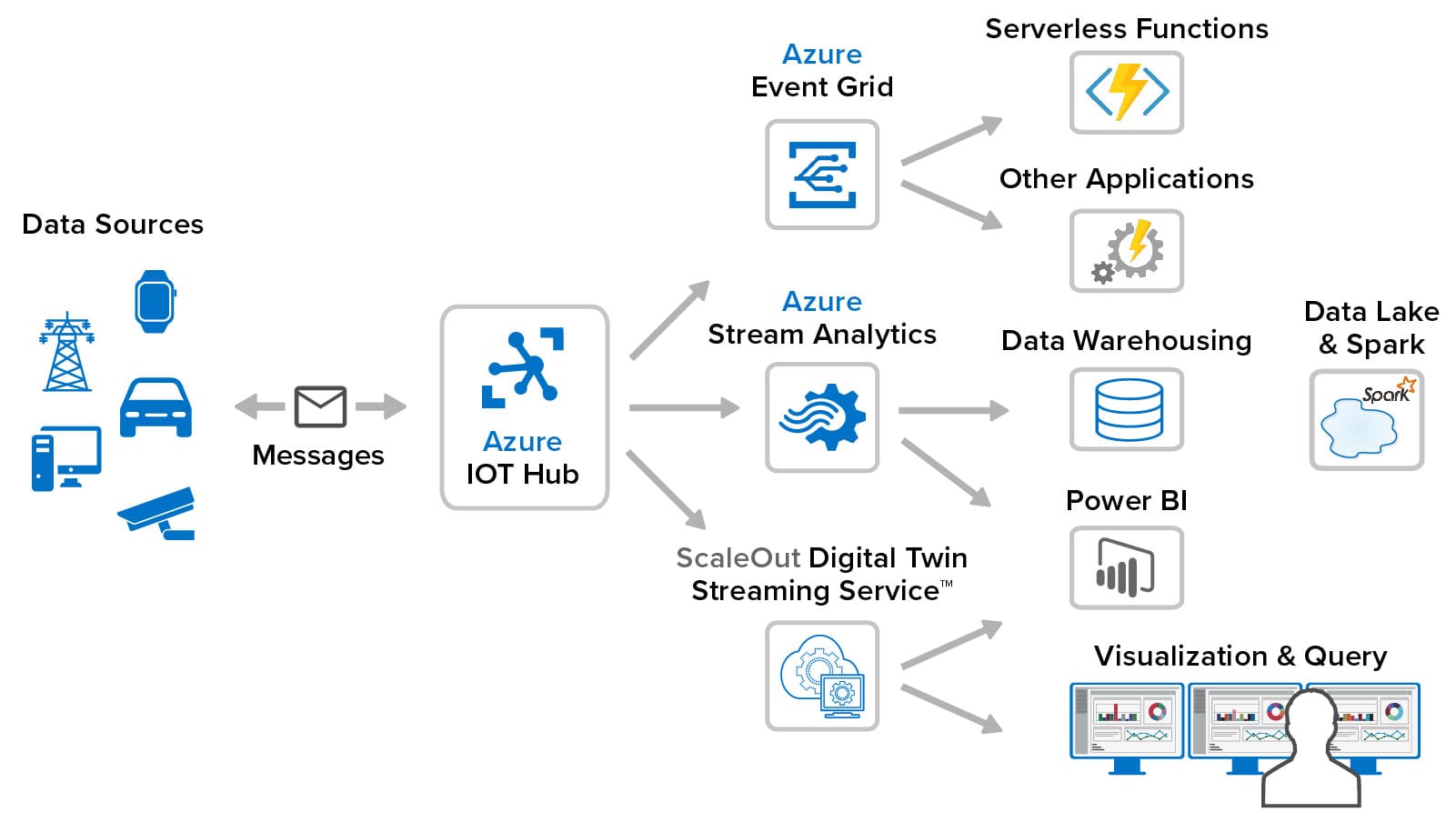
ScaleOut’s streaming service handles all the details of message delivery, data management, code orchestration, and scalable execution. This makes developing streaming analytics code for real-time digital twins fast and easy. The application developer just focuses on writing a single method to process incoming messages, run application-specific analytics, update state information about the data source, and generate alerts as needed. The optional rules engine further simplifies the development process with a UI for specifying state data and a sequential list of business rules for describing analytics code.
How are the streaming service’s real-time digital twins different from Azure digital twins? Both services leverage the digital twin concept by providing a software entity for each IoT device that can track the parameters and state of the device. What’s different is the streaming service’s focus on real-time analytics and its use of an in-memory computing platform integrated with Azure IoT Hub to ensure the lowest possible latency and high scalability. Azure digital twins serve a different purpose. They are intended to maintain a graphical representation of an organization’s entities for management and querying current status; they are not designed to implement real-time analytics using application-defined algorithms.
The following diagram illustrates the integration of ScaleOut’s streaming service with Azure IoT Hub to provide fast, scalable event handling with low-latency access to memory-based state for all data sources. It shows how real-time digital twins are distributed across multiple virtual servers organized into an in-memory computing cluster connected to Azure IoT Hub. The streaming service uses multiple message queues in Azure IoT Hub to scale message delivery and event processing:
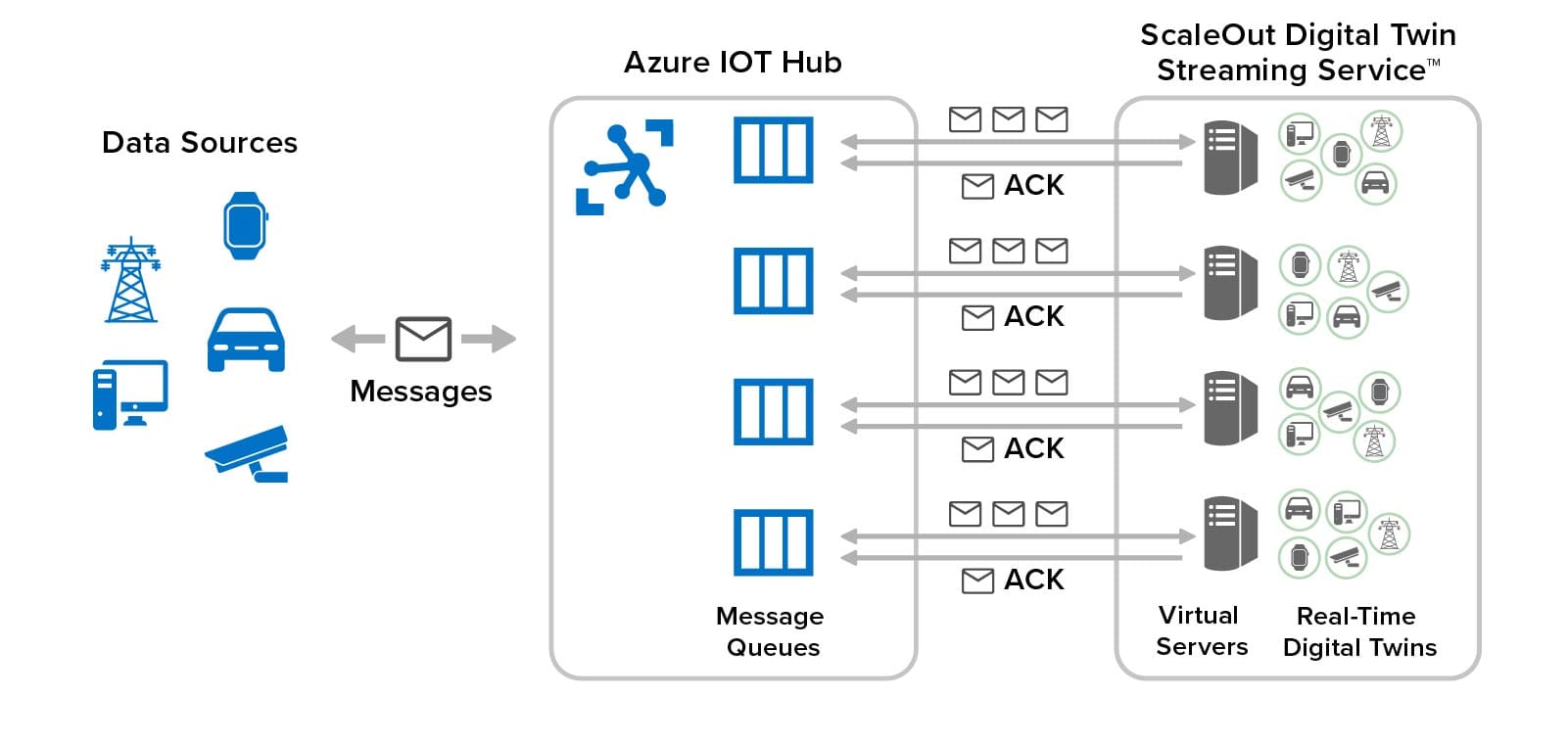
As IoT devices proliferate and become more intelligent, it’s vital that our cloud-based event-processing systems be able to perform continuous and deep introspection in real time. This enables applications to react quickly, effectively, and autonomously to emerging challenges, such as to security threats and safety issues, as well as to new opportunities, such as real-time ecommerce recommendations. While there is an essential role for query and offline analytics to optimize IoT services, the need for highly granular, real-time analytics continues to grow. ScaleOut’s Digital Twin Streaming Service is designed to meet this need as an integral part of the Azure IoT ecosystem.
To learn more about using the ScaleOut’s Digital Twin Streaming Service in the Microsoft Azure cloud, visit the Azure Marketplace here.
The post Adding New Capabilities for Real-Time Analytics to Azure IoT appeared first on ScaleOut Software.
]]>The post New Article in Security Boulevard on Real-Time Cyber Threat Assessment appeared first on ScaleOut Software.
]]>
The post New Article in Security Boulevard on Real-Time Cyber Threat Assessment appeared first on ScaleOut Software.
]]>The post New Article in RT Insights on Tracking Vaccine Distribution with Real-Time Digital Twins appeared first on ScaleOut Software.
]]>The post New Article in RT Insights on Tracking Vaccine Distribution with Real-Time Digital Twins appeared first on ScaleOut Software.
]]>The post Building the Next Generation in Physical and Cyber Security with Real-Time Digital Twins appeared first on ScaleOut Software.
]]>
In-Memory Computing with Real-Time Digital Twins Offers the Intelligence, Responsiveness, Agility, and Scalability that Security and Safety Systems are Missing
Today’s physical and cyber security systems need to quickly detect and respond to unauthorized intrusions. However, these systems typically do not take advantage of in-memory computing techniques to help them immediately assess threats and generate alerts. In-memory computing with real-time digital twins offers a powerful new tool to address these challenges. Because these software components independently analyze telemetry from each data source and maintain dynamic contextual information, they can immediately spot unwanted intrusions and generate alerts. Let’s take a look at how they can add value.
Physical Security and Safety
Consider physical security with key card access control used by countless businesses and industries. Key card access control systems rely on database servers in the back office to authorize key cards for specific card readers and to log usage. As illustrated below, this information propagates to field access panels in the buildings to minimize delays in authorizing access. However, making changes usually requires manual database updates and may take minutes or longer to propagate throughout the system.
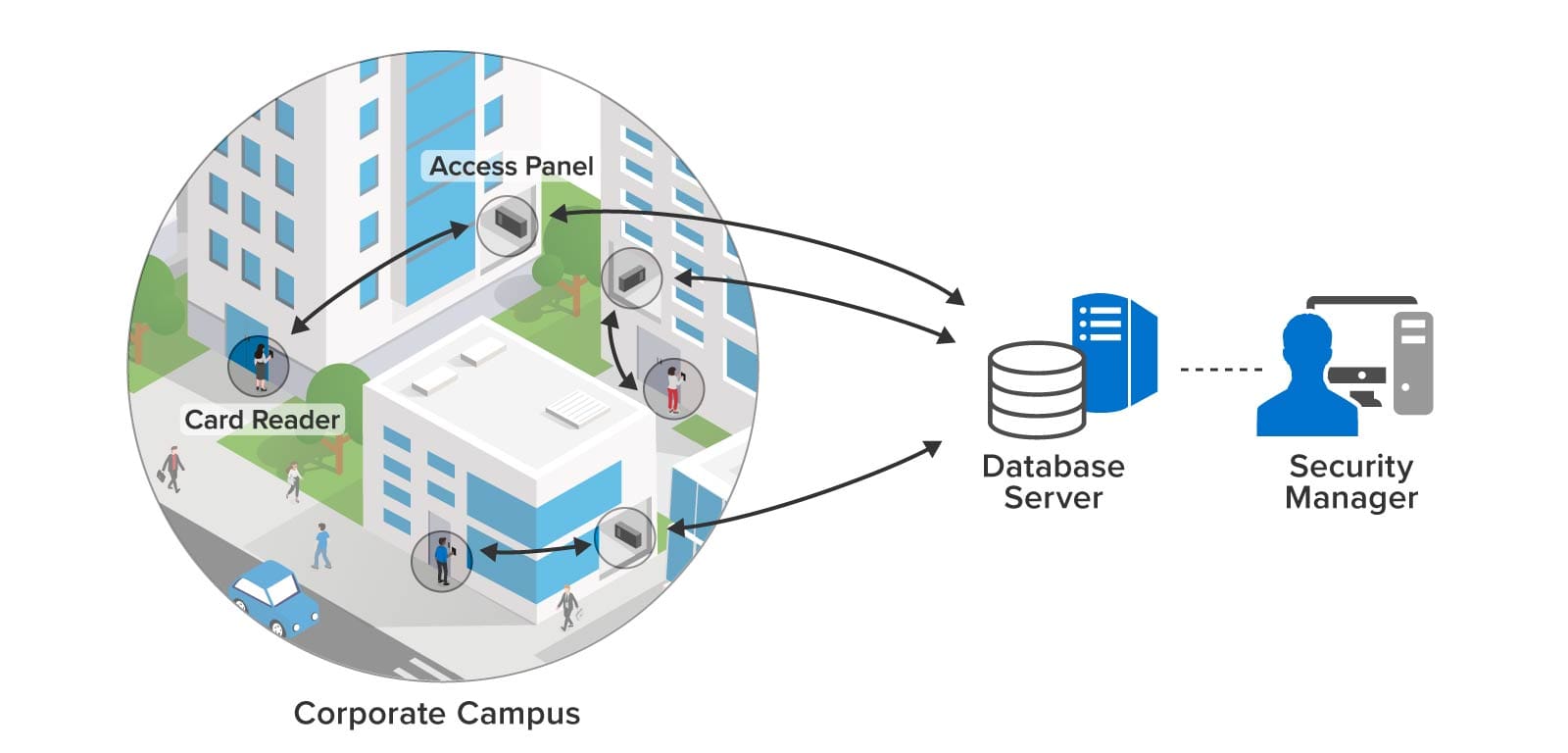
More importantly, subtle patterns of unauthorized access may escape the attention of security personnel and require a review of the logs to detect. For example, an employee who has given notice of resignation may unexpectedly visit buildings or laboratories that were not part of the employee’s known scope of work. Another employee might be put at risk by attempting to enter a hazardous laboratory without having completed the required training. An exit door might record an unusual pattern of entries outside of business hours. In all of these situations, quick detection and response could avoid unwanted intrusions or safety lapses.
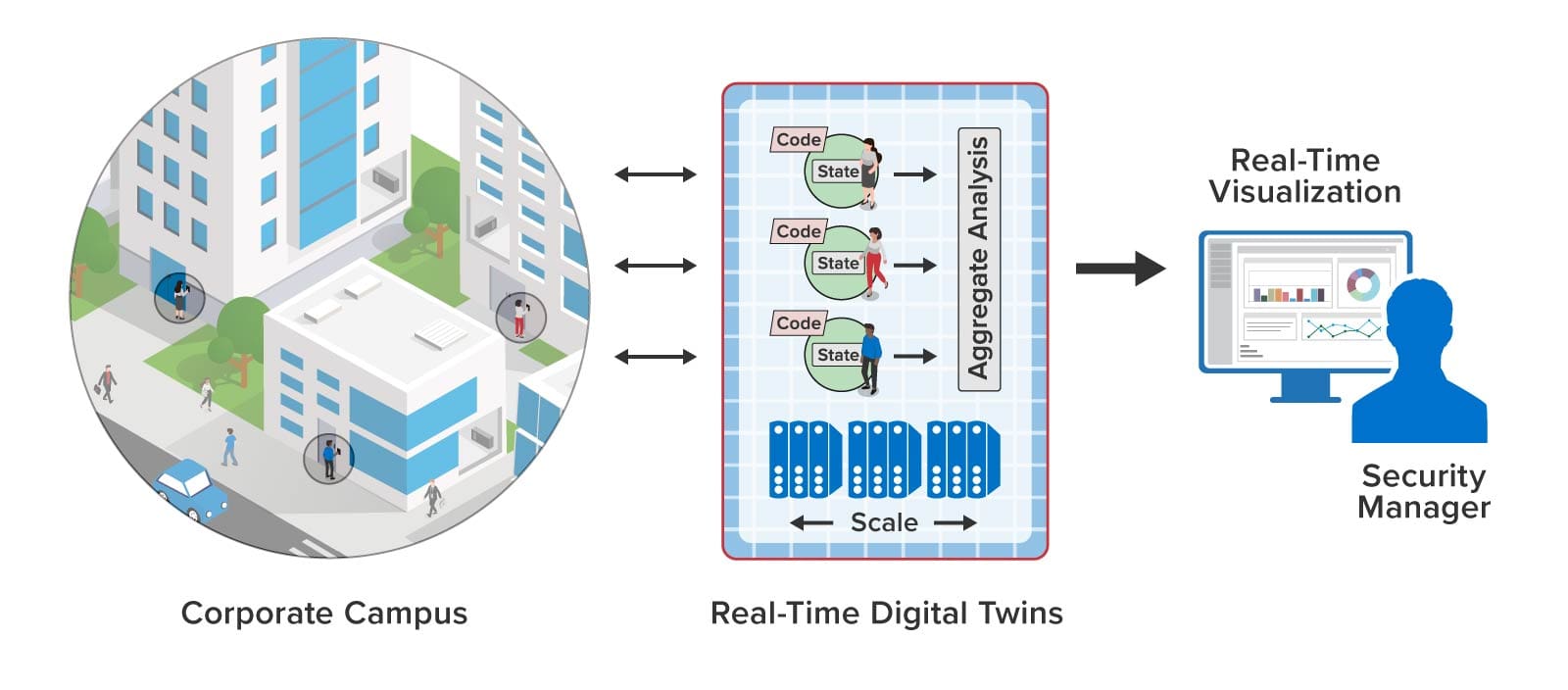
To enable immediate alerting, real-time digital twins (RTDTs) can be used to track every key card and key card reader. Since each key card is associated with a specific employee, the RTDT can track that person’s individual authorization to access buildings, entry doors, laboratories, etc. It also can track employment status and level of training to help assess safety issues. This information can be immediately updated by sending a message to the RTDT whenever the employee’s status changes. With this contextual information, each RTDT can implement highly granular access permissions at the card readers while checking authorization within several milliseconds. It also can track the employee’s and entry point’s usage patterns to look for unusual situations that should be alerted.
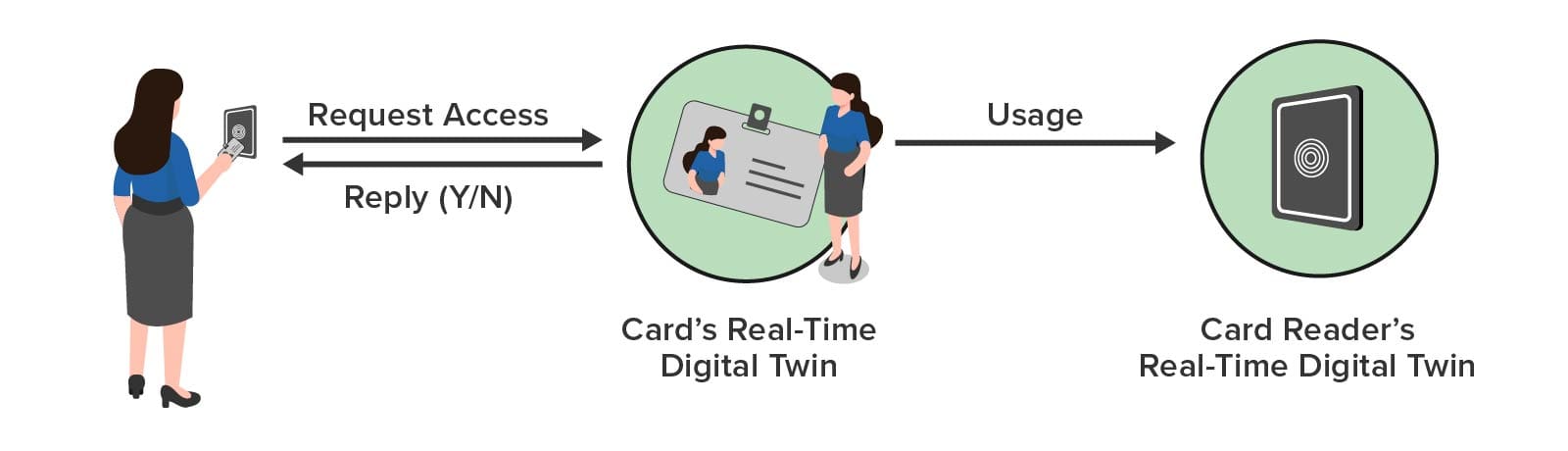
In a typical interaction, the key card reader sends a message to the employee’s key card RTDT with the reader’s identifier and time of day. After analyzing the request and tracking usage patterns, the key card RTDT responds with an authorization reply to the reader. The RTDT also sends a message to the reader’s RTDT to enable it to track usage and generate alerts as necessary, as illustrated below:
Cyber Security
Security information and event management (SIEM) software logs activities, such as user logins, failed attempts, and potentially malicious events so that security managers can detect and prevent or remediate possible intrusions. Typical SIEM software lets managers create and apply rules to event logs to extract information that should be alerted, such as identification of a chain of activity (“kill chain”) that leads to injection of malware or other malicious actions. Dashboards show managers raw telemetry, such as the number of potentially malicious events by region or events recorded over time. The forensic analysis of logs and display of large volumes of aggregated telemetry make it difficult for managers to spot and mitigate emerging kill chains, such as a chain of intrusions within a corporate infrastructure leading to an exploitation:
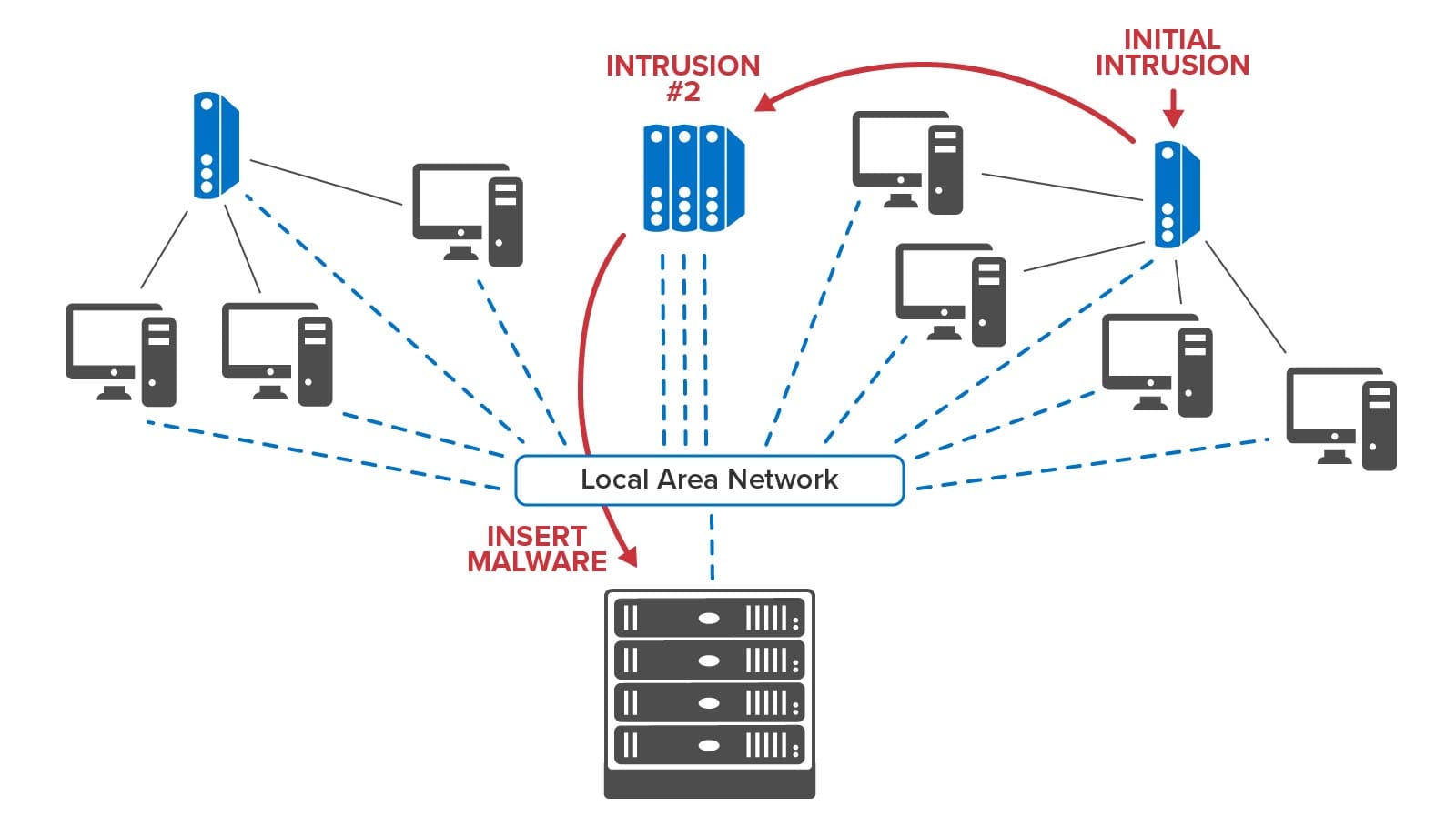
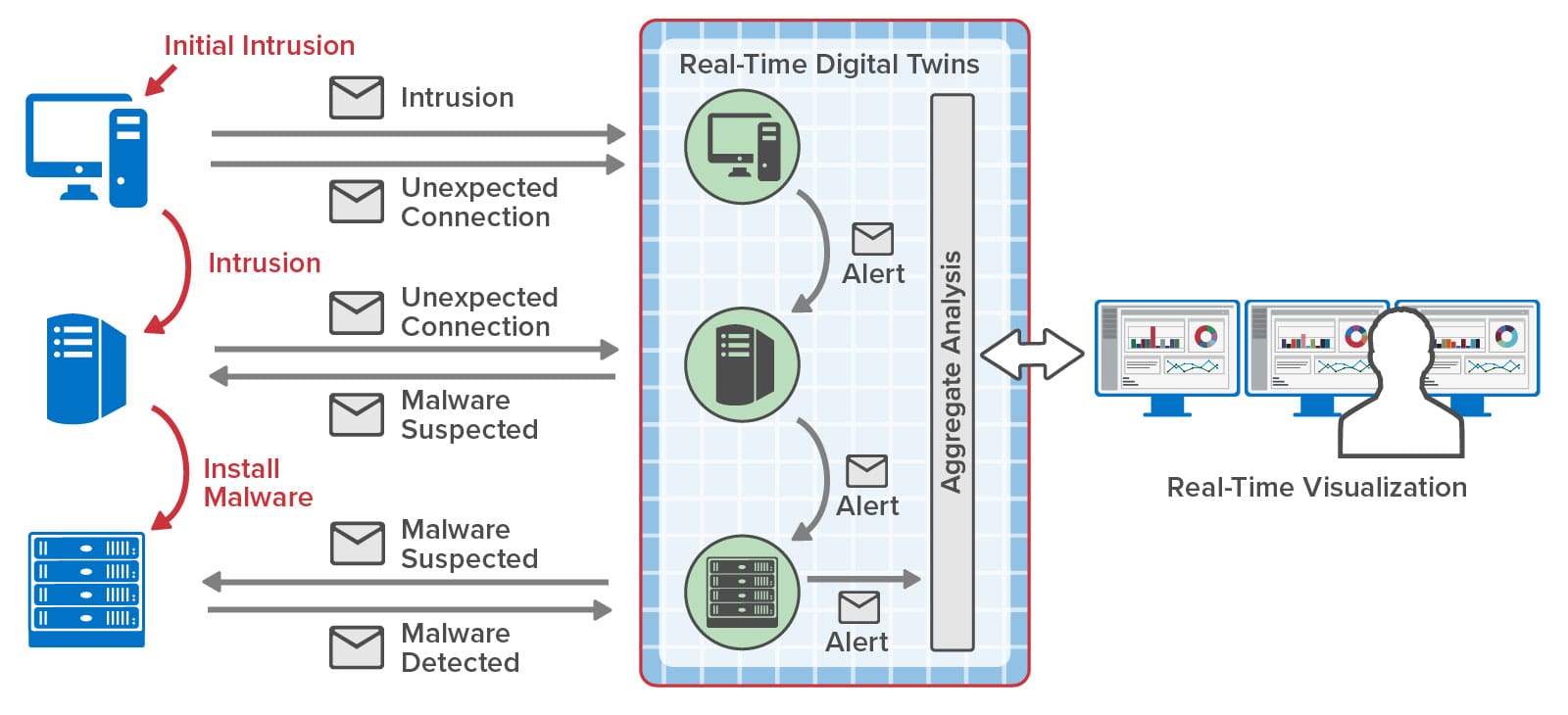
By hosting event tracking in memory with contextual information and by reacting within milliseconds to potential threats, RTDTs can help accelerate the detection and interruption of cyber kill chains. Many SIEM platforms maintain software agents distributed throughout an organization’s IT infrastructure to report suspicious events that could signal a possible intrusion. Instead of just feeding these events to a dashboard and to a log for analysis, they can also be reported to an RTDT for each agent. Each RTDT can immediately run a machine learning algorithm to classify activity and signal alerts when a threat is predicted. Moreover, if an agent’s event includes information about an outbound connection to another node in the network, the RTDT can send a message to that node’s RTDT to enrich its context and assist in detection of a potential kill chain. By dynamically sending messages to and among RTDTs that attempt to track the progression of an intruder within a network, RTDTs can build a real-time map of potential kill chains and possibly get ahead of the intruder to block threats.
The following diagram illustrates the use of RTDTs to map the progression of incoming threats as they migrate among nodes of an organization’s infrastructure:
Summing Up
Physical and cyber security systems, as well as safety systems, require simultaneous, real-time assessment of numerous interactions in the context of allowed and expected usage patterns. Instead of relying on today’s offline computing techniques and forensic analysis to perform the bulk of the work, these systems can dramatically boost their effectiveness by employing next generation in-memory computing techniques, such as real-time digital twins. This software architecture offers a highly attractive combination of intelligence, agility, responsiveness, and scalability to meet the ever-increasing challenges faced by today’s security and safety systems.
The post Building the Next Generation in Physical and Cyber Security with Real-Time Digital Twins appeared first on ScaleOut Software.
]]>The post Introducing Geospatial Mapping for Real-Time Digital Twins appeared first on ScaleOut Software.
]]>
The goal of real-time streaming analytics is to get answers fast. Mission-critical applications that manage large numbers of live data sources need to quickly sift through incoming telemetry, assess dynamic changes, and immediately pinpoint emerging issues that need attention. Examples abound: a telematics application tracking a fleet of vehicles, a vaccine distribution system managing the delivery of thousands of shipments, a security or safety application analyzing entry points in a large infrastructure (physical or cyber), a healthcare application tracking medical telemetry from a population of wearable devices, a financial services application watching wire transfers and looking for potential fraud — the list goes on. In all these cases, when a problem occurs (or an opportunity emerges), managers need answers now.
Conventional streaming analytics platforms are unable to separate messages from each data source and analyze them as they flow in. Instead, they ingest and store telemetry from all data sources, attempt a preliminary search for interesting patterns in the aggregated data stream, and defer detailed analysis to offline batch processing. As a result, they are unable to introspect on the dynamic, evolving state of each data source and immediately alert on emerging issues, such as the impending failure of a truck engine, an unusual pattern of entries and exits to a secure building, or a potentially dangerous pattern of telemetry for a patient with a known medical condition.
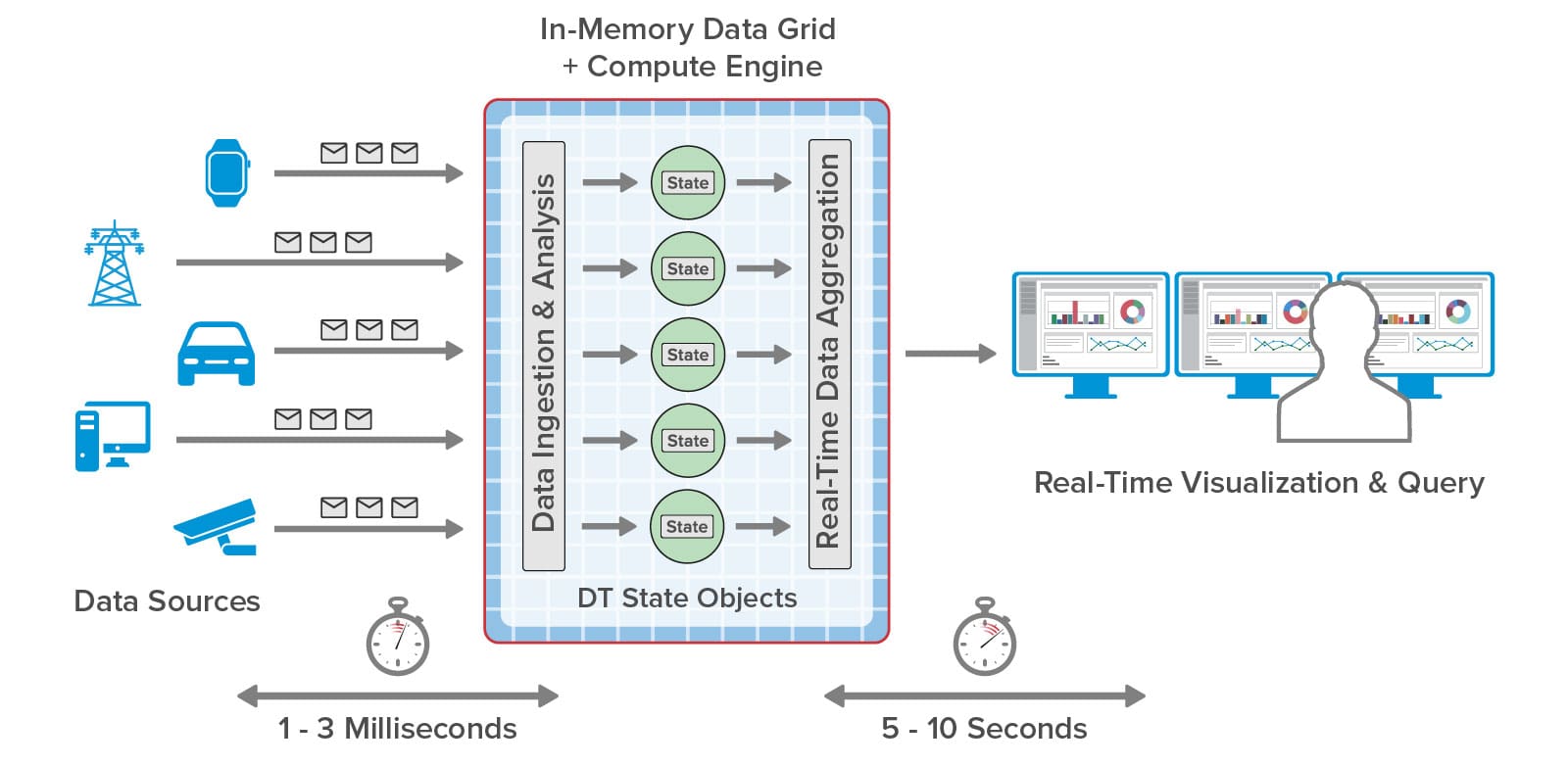
In-memory computing with software components called real-time digital twins overcomes these obstacles and enables continuous analysis of incoming telemetry for each data source with contextual information that deepens introspection. While processing each message in a few milliseconds, this technology automatically scales to simultaneously handle thousands of data sources. It also can aggregate and visualize the results of analysis every few seconds so that managers can graphically track the state of a complex live system and quickly pinpoint issues.
The ScaleOut Digital Twin Streaming Service is an Azure-based cloud service that uses real-time digital twins to perform continuous data ingestion, analysis by data source, aggregation, and visualization, as illustrated below. What’s key about this approach is that the system visualizes state information that results from real-time analysis — not raw telemetry flowing in from data sources. This gives managers curated data that intelligently focuses on the key problem areas (or opportunities). For example, instead of looking at fluctuating oil temperature, telematics dispatchers see the results of predictive analytics. There’s not enough time for managers to examine all the raw data, and not enough time to wait for batch processing to complete. Maintaining situational awareness requires real-time introspection for each data source, and real-time digital twins provide it.
is an Azure-based cloud service that uses real-time digital twins to perform continuous data ingestion, analysis by data source, aggregation, and visualization, as illustrated below. What’s key about this approach is that the system visualizes state information that results from real-time analysis — not raw telemetry flowing in from data sources. This gives managers curated data that intelligently focuses on the key problem areas (or opportunities). For example, instead of looking at fluctuating oil temperature, telematics dispatchers see the results of predictive analytics. There’s not enough time for managers to examine all the raw data, and not enough time to wait for batch processing to complete. Maintaining situational awareness requires real-time introspection for each data source, and real-time digital twins provide it.
In the ScaleOut Digital Twin Streaming Service, real-time data visualization can take the form of charts and tables. Dynamic charts effectively display the results of aggregate analytics that combine data from all real-time digital twins to show emerging patterns, such as the regions of the country with the largest delivery delays for a vaccine distribution system. This gives a comprehensive view that helps managers maintain the “big picture.” To pinpoint precisely which data sources need attention, users can query analytics results for all real-time digital twins and see the results in a table. This enables managers to ask questions like “Which vaccination centers in Washington state are experiencing delivery delays in excess of 1 hour and have seen more than 100 people awaiting vaccinations at least three times today?” With this information, managers can immediately determine where vaccine shipments should be delivered first.
With the latest release, the streaming service now offers geospatial mapping of query results combined with continuous queries that refresh the map every few seconds. For example, using this cloud service, a telematics system for a trucking fleet can continuously display the locations of specific trucks which have issues (the red dots on the map) in addition to watching aggregate statistics:
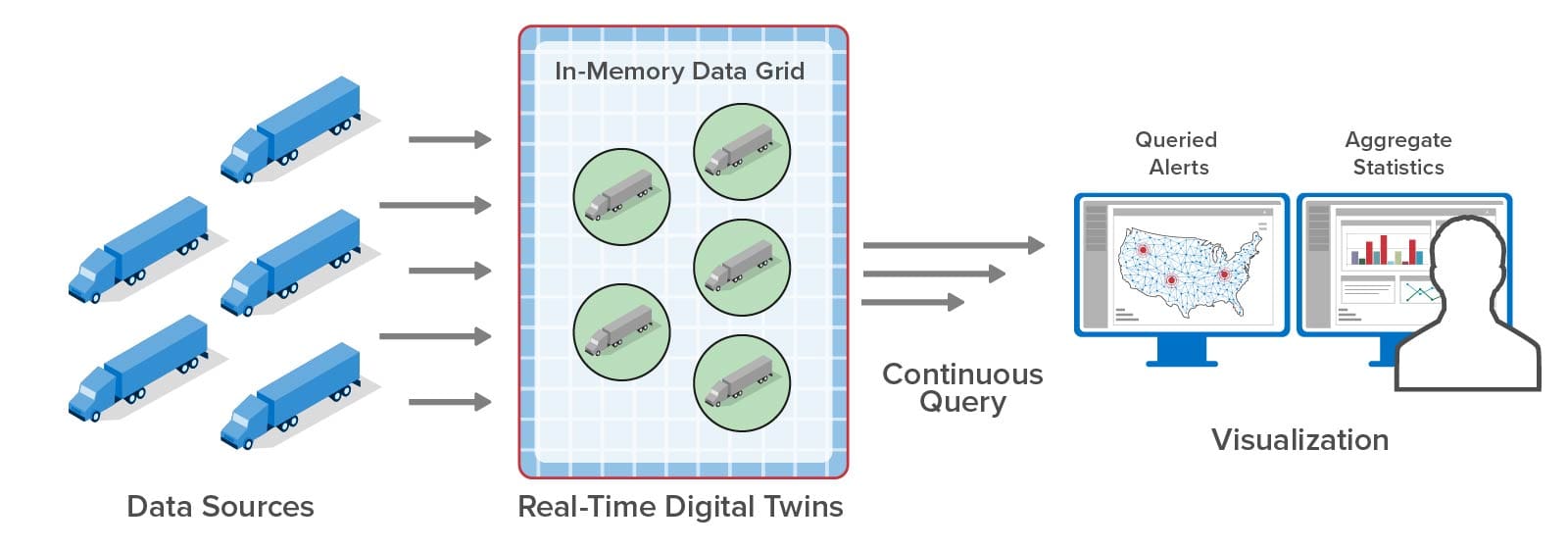
For applications like this, a mapped view of query results offers valuable insights about the locations where issues are emerging that would otherwise be more difficult to obtain from a tabular view. Note that the queried data shows the results of real-time analytics which are continuously updated as messages arrive and are processed. For example, instead of displaying the latest oil temperature from a truck, the query reports the results of a predictive analytics algorithm that makes use of several state variables maintained by the real-time digital twin. This declutters the dispatcher’s view so that only alertable conditions are highlighted and demand attention:
The following image shows an example of actual map output for a hypothetical security application that tracks possible intrusions within a nationwide power grid. The goal of the real-time digital twins is to assess telemetry from each of 20K control points in the power grid’s network, filter out false-positives and known issues, and produce a quantitative assessment of the threat (“alert level”). Continuous queries map the results of this assessment so that managers can immediately spot a real threat, understand its scope, and take action to isolate it. The map shows the results of results three continuous queries: high alerts requiring action, medium alerts that just need watching, and offline nodes (with the output suppressed here):
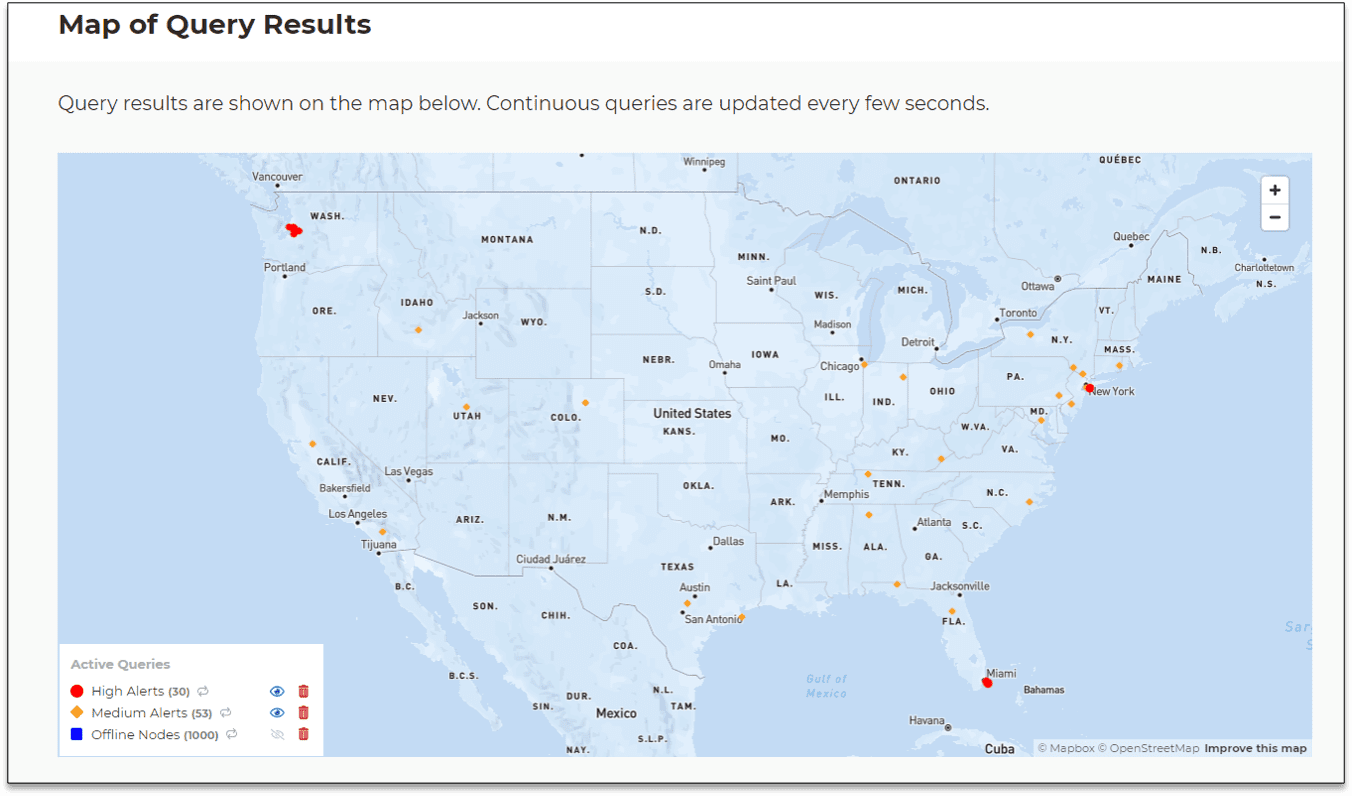
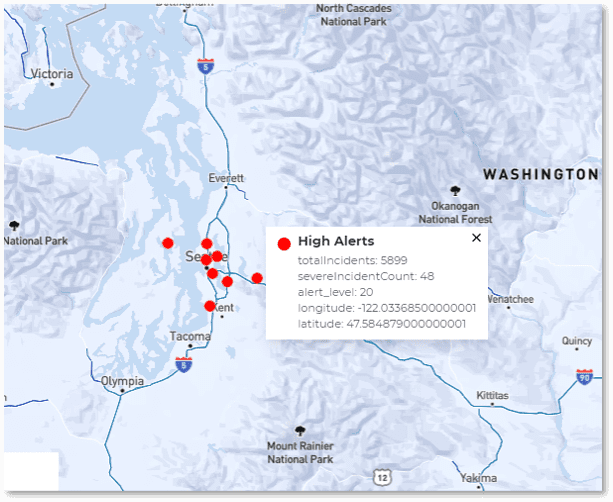
In this scenario a high alert has suddenly appeared in the grid at three locations (Seattle, New York, and Miami) indicating a serious, coordinated attack on the network. By zooming in and hovering over dots in the graph, users can display the detailed query results for each corresponding data source. Within seconds, managers have immediate, actionable information about threat assessments and can quickly visualize the locations and scope of specific threats.
In applications like these and many others, the power of in-memory computing with real-time digital twins gives managers a new means to digest real-time telemetry from thousands of data sources, combine it with contextual information that enhances the analysis, and then immediately visualize the results. This powerful technology boosts situational awareness and helps guide responses much better and faster than was previously possible.
The post Introducing Geospatial Mapping for Real-Time Digital Twins appeared first on ScaleOut Software.
]]>The post Deploying Real-Time Digital Twins On Premises with ScaleOut StreamServer DT appeared first on ScaleOut Software.
]]>
With the ScaleOut Digital Twin Streaming Service , an Azure-hosted cloud service, ScaleOut Software introduced breakthrough capabilities for streaming analytics using the real-time digital twin concept. This new software model enables applications to easily analyze telemetry from individual data sources in 1-3 milliseconds while maintaining state information about data sources that deepens introspection. It also provides a basis for applications to create key status information that the streaming platform aggregates every few seconds to maximize situational awareness. Because it runs on a scalable, highly available in-memory computing platform, it can do all this simultaneously for hundreds of thousands or even millions of data sources.
, an Azure-hosted cloud service, ScaleOut Software introduced breakthrough capabilities for streaming analytics using the real-time digital twin concept. This new software model enables applications to easily analyze telemetry from individual data sources in 1-3 milliseconds while maintaining state information about data sources that deepens introspection. It also provides a basis for applications to create key status information that the streaming platform aggregates every few seconds to maximize situational awareness. Because it runs on a scalable, highly available in-memory computing platform, it can do all this simultaneously for hundreds of thousands or even millions of data sources.
The unique capabilities of real-time digital twins can provide important advances for numerous applications, including security, fleet telematics, IoT, smart cities, healthcare, and financial services. These applications are all characterized by numerous data sources which generate telemetry that must be simultaneously tracked and analyzed, while maintaining overall situational awareness that immediately highlights problems of concern an/or opportunities of interest. For example, consider some of the new capabilities that real-time digital twins can provide in fleet telematics and vaccine distribution during COVID-19.
To address security requirements or the need for tight integration with existing infrastructure, many organizations need to host their streaming analytics platform on-premises. Scaleout StreamServer® DT was created to meet this need. It combines the scalable, battle-tested in-memory data grid that powers ScaleOut StreamServer with the graphical user interface and visualization features of the cloud service in a unified, on-premises deployment. This gives users all of the capabilities of the ScaleOut Digital Twin Streaming Service with complete infrastructure control.
As illustrated in the following diagram, ScaleOut StreamServer DT installs its management console on a standalone server that connects to ScaleOut StreamServer’s in-memory data grid. This console hosts the graphical user interface that is securely accessed by remote workstations within an organization. It also deploys real-time digital twin models to the in-memory data grid, which hosts instances of digital twins (one per data source) and runs application-defined code to process incoming messages. Message are delivered to the grid using messaging hubs, such as Azure IoT Hub, AWS IoT Core, Kafka, a built-in REST service, or directly using APIs.
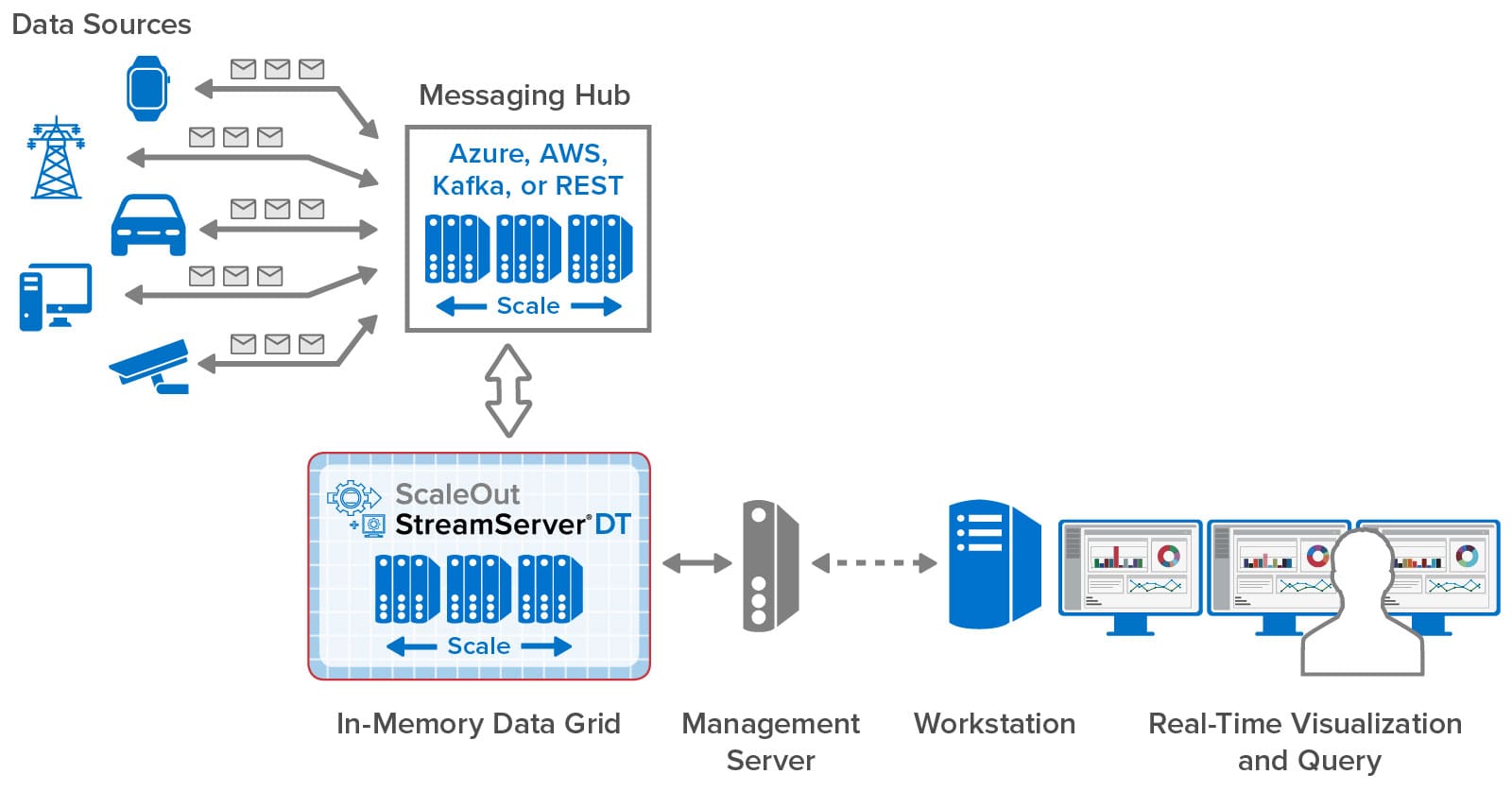
The management console installs as a set of Docker containers on the management server. This simplifies the installation process and ensures portability across operating systems. Once installed, users can create accounts to control access to the console, and all connections are secured using SSL. The results of aggregate analytics and queries performed within the in-memory data grid can then be accessed and visualized on workstations running throughout an organization.
Because ScaleOut’s in-memory data grid runs in an organization’s data center and avoids the requirement to use a cloud-hosted message hub or REST service, incoming messages from data sources can be processed with minimum latency. In addition, application code running in real-time digital twins can access local resources, such as databases and alerting systems, with the best possible performance and security. Use of dedicated computing resources for the in-memory data grid delivers the highest possible throughput for message processing and real-time analytics.
While cloud hosting of streaming analytics as a SaaS (software-as-a-service) offering creates clear advantages in reducing capital costs and providing access to highly elastic computing resources, it may not be suitable for organizations which need to maintain full control of their infrastructures to address security and performance requirements. ScaleOut StreamServer DT was designed to meet these needs and deliver the important, unique benefits of streaming analytics using real-time digital twins to these organizations.
The post Deploying Real-Time Digital Twins On Premises with ScaleOut StreamServer DT appeared first on ScaleOut Software.
]]>The post ScaleOut Named as Leading Innovator for Stream Processing appeared first on ScaleOut Software.
]]> , ScaleOut’s ground-breaking, Azure-hosted cloud service leverages the power of in-memory computing to let applications track hundreds of thousands of data sources (or more) in real time. With its ability to deepen introspection on the state of data sources and visualize aggregate trends within seconds, this cloud service opens up important new capabilities for a wide range of applications, including those in telematics, logistics, cyber/physical security, IoT, smart cities, financial services, and much more.
, ScaleOut’s ground-breaking, Azure-hosted cloud service leverages the power of in-memory computing to let applications track hundreds of thousands of data sources (or more) in real time. With its ability to deepen introspection on the state of data sources and visualize aggregate trends within seconds, this cloud service opens up important new capabilities for a wide range of applications, including those in telematics, logistics, cyber/physical security, IoT, smart cities, financial services, and much more.
The power of this breakthrough new technology has gained the attention of leading industry analysts. In their recent Data Management: IoT Stream Processing and Streaming Analytics competitive ranking report, ABI Research named ScaleOut Software as the leading vendor in innovation “owing to its highly effective Digital Twin Streaming Service that can track telemetry streams, data aggregation tools, and trend recognition capabilities of multiple devices’ telemetry.”
The full press release from ABI Research can be found here.
The post ScaleOut Named as Leading Innovator for Stream Processing appeared first on ScaleOut Software.
]]>The post ScaleOut Software Joins Digital Twin Consortium to Share Streaming Analytics Expertise appeared first on ScaleOut Software.
]]>BELLEVUE, Wash – March 2, 2021 – ScaleOut Software today announced that it has joined Digital Twin Consortium to help define and advance the use of digital twin technologies across various industries.
“We are excited to join the Digital Twin Consortium,” said Dr. William L. Bain, founder, and CEO of ScaleOut Software. “We believe that digital twins offer great promise across numerous industries from telematics to IIoT, healthcare, physical security and eCommerce. They can dramatically improve situational awareness for managers of live systems spanning thousands or even millions of data sources, and we are delighted to help raise awareness of the concept of harnessing digital twins for streaming analytics via the Consortium.”
As defined by Digital Twin Consortium, the digital twin concept encompasses use cases for both product lifecycle management (PLM), where the idea originated, and for real-time streaming analytics for live systems. ScaleOut Software’s real-time digital twin technology represents the latter approach and adopts this concept for streaming analytics. The company’s “real-time digital twin” software architecture for streaming analytics across industries provides more informed decision making in the moment for applications that track thousands of data sources.
Real-time digital twins create a “model” of each individual data source as they track the specific characteristics relevant for the goals of streaming analytics, such as detecting anomalous conditions or predicting failures. This generalization of the modeling concept allows digital twins to analyze not only physical devices but also a wide array of data sources that would not be typically considered, such as ecommerce shoppers for a recommendation system.
“We welcome ScaleOut Software to Digital Twin Consortium,” said Executive Director, Dr. Richard Soley. “Their knowledge of real-time digital twin software and streaming analytics will be very valuable to our members as we work together to advance digital twin technologies.”
Harnessing the Digital Twin Model
ScaleOut Software’s streaming analytics platform leverages the digital twin concept by associating a software component, called a “real-time digital twin,” with every data source to analyze the incoming telemetry from that data source. Large systems, such as trucking fleets or access control systems, often require thousands of data sources to be simultaneously monitored. Each real-time digital twin maintains dynamic state information that assists in predictive analytics and other use cases. This enables deeper inferencing about the evolving state of each data source than otherwise possible.
When run on a scalable, in-memory computing platform, real-time digital twins dramatically increase the amount of analysis that can be performed as telemetry arrives, and they avoid the delays incurred by offline, big-data analytics. The in-memory platform can simultaneously host thousands or even millions of digital twins to ensure predictable response times, and it can continuously aggregate state information for immediate visualization.
Benefits of Real-Time Digital Twins for Streaming Analytics
Real-time digital twins:
- Provide Immediate, Contextual Insights: Real-time digital twins allow the telemetry from a large population of data sources to be immediately and independently tracked, analyzed, and filtered, while making use of dynamically evolving contextual information. They enable feedback and alerts to be generated within a few milliseconds.
- Aggregate Insights to Identify Trends and Issues: Real-time digital twins maintain dynamic state information that can be aggregated and visualized to identify important trends or issues within seconds. This capability dramatically boosts overall situational awareness for managers of live systems.
- Simplify Development and Deployment: Real-time digital twins offer a compelling technique for simplifying application code and shortening design time. The digital twin model can be implemented using well understood, standard, object-oriented techniques that encapsulate analytics code and state information. This enables fast development and agility to meet evolving requirements.
For more information, please visit www.scaleoutsoftware.com and follow @ScaleOut_Inc on Twitter.
Additional Resources:
- ScaleOut Digital Twin Streaming Service Product Page
- Announcing the ScaleOut Digital Twin Streaming Service
 Blog Post
Blog Post - Developing Real-Time Digital Twins for Cloud Deployment Blog Post
About ScaleOut Software
Founded in 2003, ScaleOut Software develops leading-edge software that delivers scalable, highly available, in-memory computing and streaming analytics technologies to a wide range of industries. ScaleOut Software’s in-memory computing platform enables operational intelligence by storing, updating, and analyzing fast-changing, live data so that businesses can capture perishable opportunities before the moment is lost. It has offices in Bellevue, Washington and Beaverton, Oregon.
###
Contact:
RH Strategic for ScaleOut Software
206-264-0246
The post ScaleOut Software Joins Digital Twin Consortium to Share Streaming Analytics Expertise appeared first on ScaleOut Software.
]]>The post Real-Time Digital Twins Can Help Expedite Vaccine Distribution appeared first on ScaleOut Software.
]]>Agile In-Memory Software Can Track the Dynamic Rollout of Vaccine Distribution and Delivery to Quickly Spot Problems
Getting the COVID-19 crisis under control requires that we put in place an effective process for vaccine distribution so that the country can get to herd immunity as fast as possible. We are faced with quickly building a nationwide logistics network and standing up well more than 50,000 vaccination centers. Making all this work smoothly means that managers need accurate, up-to-the-minute information about all aspects of this operation, including:
- Where are all the vaccine shipments right now?
- What is the shortfall in vaccines at each center?
- How many people are waiting for vaccines at each center?
- How many qualified personnel are available at each center?
- Which centers have the most urgent needs and need immediate attention?
- Is vaccine distribution underserving certain regions or population groups?
Given the unique and highly dynamic nature of this challenge, we need software solutions that are agile enough to adapt to evolving needs and scalable enough to quickly handle a daunting amount of fast-changing data. Conventional, enterprise data architectures take months to develop and are complex to change. Is there a simpler, faster way to wrangle this data for crisis managers?
In-Memory Computing with Real Time Digital Twins: Fast and Agile
A software technology called in-memory computing has evolved over the last twenty years to grapple with the challenge of tracking and analyzing fast-changing data. Its two core competencies are speed and scalability. Widely used to track ecommerce shopping carts, financial transactions, airline flights and much more, in-memory computing can quickly store, retrieve, and analyze large volumes of live data. This powerful technology may also be just what we need to help tackle the challenge of vaccine distribution.
In the last two years, the concept of real-time digital twins has emerged to let in-memory computing track incoming data streams from hundreds of thousands of data sources, maintain pertinent information about each data source, and immediately alert when unusual conditions are detected. The power of this approach lies in its ability to simplify the problem for application developers. It encapsulates code that just focuses on analyzing messages from a single data source as they flow in, and it maintains an up-to-the second assessment of the data source’s status. Real-time digital twins are both easy to develop and easy to change as needs evolve. The in-memory computing system which hosts them typically runs as a cloud service (such as the ScaleOut Digital Twin Streaming Service) that transparently scales to handle as many data sources as needed.
Real-Time Digital Twins Can Help Expedite Vaccine Distribution
To track the distribution and delivery of COVID-19 vaccines, a real-time digital twin can be deployed for each shipment in transit and for each vaccination center. For shipments, the digital twins can track location, destination, and current condition on a second-by-second basis, allowing managers to instantly know where a shipment is and whether its viability is at risk, for example, due to a temperature change. For vaccination centers, real-time digital twins can track location, the supply of vaccines, current demand (number of recipients), availability of trained personnel to perform injections, and other parameters. Code in the digital twin continuously analyzes incoming messages to determine whether a problem exists or is likely to occur, and it alerts managers to urgent issues within a few milliseconds. This allows managers to keep track of which of the 50,000 centers need immediate assistance.
The following diagram illustrates the use of real-time digital twins to track thousands of vaccine shipments and vaccination centers. The red dotted lines depict message streams flowing from data sources located throughout the country over the Internet to their corresponding real-time digital twins hosted in the cloud service.
![]()
Let’s take a closer look at the real-time digital twin for a vaccination center. Using a simple web app, personnel at the vaccination center send periodic messages updating information about supplies, personnel, recipients, and wait times. The real time digital twin for this center records this data and then analyzes it for issues, such as a shortfall in supplies, lack of available personnel, or a surge in incoming recipients. It can then compute an assessment of the urgency for assistance (call it an alert level) which can be compared to other centers to identify which ones have the most urgent issues. If the alert level becomes sufficiently high, the analysis code can immediately notify managers. By analyzing incoming messages, real-time digital twins keep track of the latest status for all vaccination centers.
Here’s an illustration of a vaccination center sending messages to its real-time digital twin running in the cloud. It shows some of the state information that the twin maintains and the code which analyzes incoming messages as they arrive:
![]()
Aggregate Analytics Boost Situational Awareness
When dealing with thousands of dynamic data sources, managers can use real-time digital twins to serve as highly responsive watchdogs that continuously evaluate incoming information for changes that may need attention. This helps managers easily track thousands of data sources and focus on the most pressing concerns.
To further boost situational awareness, the in-memory computing platform can group and aggregate data held in the real-time digital twins every few seconds to help surface widespread changes that need strategic responses. For example, the average shortfall in vaccine doses for all centers in each region of the country can be aggregated to track where shortfalls may be occurring. This information can be visualized as shown in the chart below, which is updated every few seconds to provide managers with the most current view of the situation:
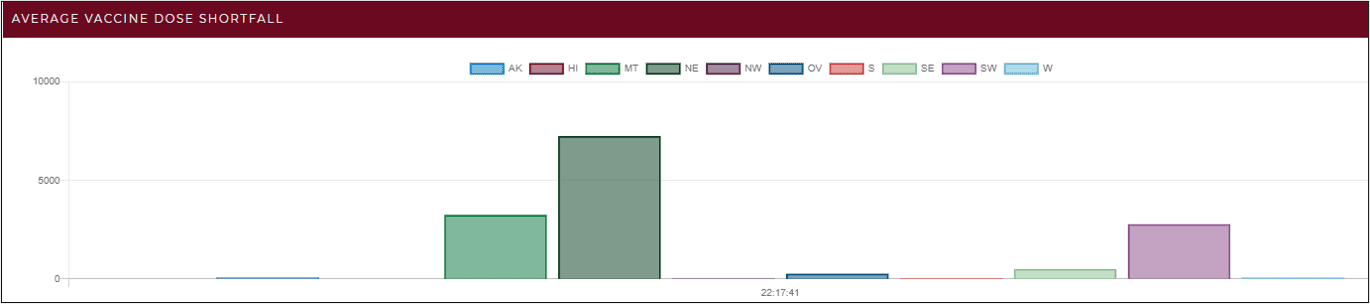
Likewise, this technique can be used to aggregate the average wait times for all vaccination centers by county. This can help determine where bottlenecks in vaccine delivery are occurring and enable mangers to render assistance by relocating personnel from less busy centers to overwhelmed ones.
Aggregate analytics of data maintained by real-time digital twins can also be used to track and validate the equitable distribution of vaccines. For example, it can aggregate information collected from each center about the demographics of vaccine recipients, such as age and ethnicity, and characteristics of the centers themselves, such as hospitals vs pharmacies and urban vs rural. This allows key real-time statistics to be tracked, such whether certain groups or regions are being underserved and whether hospitals have shorter wait times than pharmacies.
Summing Up
Without a doubt, distributing and delivering COVID-19 vaccines quickly and effectively over the next few months presents formidable challenges, namely:
- Ensuring that logistics managers get the critical information they need in a timely manner
- Avoiding the complexity and delay required to build custom information management systems that can provide this information
Because it is fast, scalable, and agile, in-memory computing technology with real-time digital twins can serve as a valuable tool for tracking the status of many thousands of vaccination centers and shipments. This innovative software infrastructure can quickly be programmed to analyze vital parameters and statistics in milliseconds and aggregate key data every few seconds. It offers managers a powerful and flexible means for helping ensure fast, efficient vaccine distribution and delivery.
The post Real-Time Digital Twins Can Help Expedite Vaccine Distribution appeared first on ScaleOut Software.
]]>The post Use Digital Twins for the Next Generation in Telematics appeared first on ScaleOut Software.
]]>
Real-Time Digital Twins Can Add Important New Capabilities to Telematics Systems and Eliminate Scalability Bottlenecks
Rapid advances in the telematics industry have dramatically boosted the efficiency of vehicle fleets and have found wide ranging applications from long haul transport to usage-based insurance. Incoming telemetry from a large fleet of vehicles provides a wealth of information that can help streamline operations and maximize productivity. However, telematics architectures face challenges in responding to telemetry in real time. Competitive pressures should spark innovation in this area, and real-time digital twins can help.
Current Telematics Architecture
The volume of incoming telemetry challenges current telematics systems to keep up and quickly make sense of all the data. Here’s a typical telematics architecture for processing telemetry from a fleet of trucks:
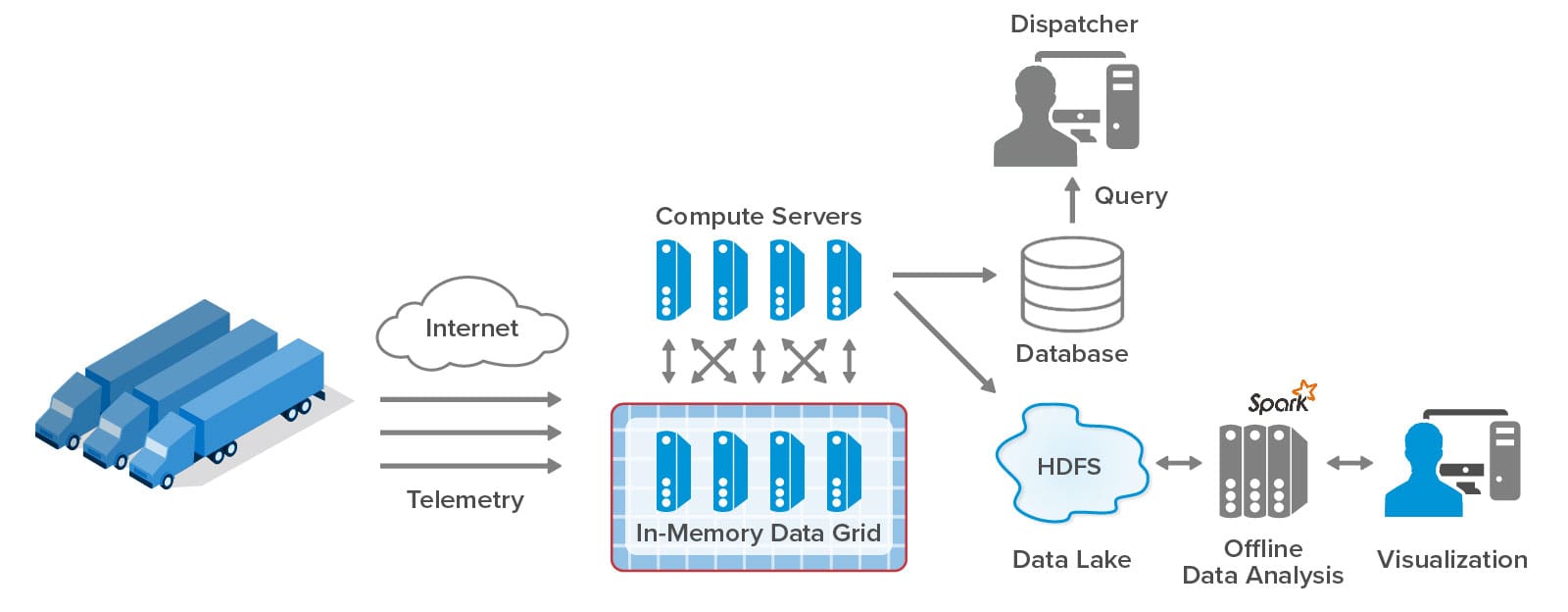
Each truck today has a microprocessor-based sensor hub which collects key telemetry, such as vehicle speed and acceleration, engine parameters, trailer parameters, and more. It sends messages over the cell network to the telematics system, which uses its compute servers (that is, web and application servers) to store incoming messages as snapshots in an in-memory data grid, also known as a distributed cache. Every few seconds, the application servers collect batches of snapshots and write them to the database where they can be queried by dispatchers managing the fleet. At the same time, telemetry snapshots are stored in a data lake, such as HDFS, for offline batch analysis and visualization using big data tools like Spark. The results of batch analysis are typically produced after an hour’s delay or more. Lastly, all telemetry is archived for future use (not shown here).
This telematics architecture has evolved to handle ever increasing message rates (often reaching 2K messages per second), make up-to-the-minute information available to dispatchers, and feed offline analytics. Using a database, dispatchers can query raw telemetry to determine the information they need to manage the fleet in real time. This enables them to answer questions such as:
- “Where is truck 7563?”
- “How long has the driver been on the road?”
- “Which trucks have abnormally high oil temperature?”
Offline analytics can mine the telemetry for longer term statistics that help managers assess the fleet’s overall performance, such as the average length of delivery or routing delays, the fleet’s change in fuel efficiency, the number of drivers exceeding their allowed shift times, and the number and type of mechanical issues. These statistics help pinpoint areas where dispatchers and other personnel can make strategic improvements.
Challenges for Current Architectures
There are three key limitations in this telematics architecture which impact its ability to provide managers with the best possible situational awareness. First, incoming telemetry from trucks in the fleet arrives too fast to be analyzed immediately. The architecture collects messages in snapshots but leaves it to human dispatchers to digest this raw information by querying a database. What if the system could separately track incoming telemetry for each truck, look for changes based on contextual information, and then alert dispatchers when problems were identified? For example, the system could perform continuous predictive analytics on the engine’s parameters with knowledge of the engine’s maintenance history and signal if an impending failure was detected. Likewise, it could watch for hazardous driving with information about the driver’s record and medical condition. Having the system continuously introspect on the telemetry for each truck would enable the dispatcher to spot problems and intervene more quickly and effectively.
A second key limitation is the lack of real-time aggregate analysis. Since this analysis must be performed offline in batch jobs, it cannot respond to immediate issues and is restricted to assessing overall fleet performance. What if the real-time telemetry tracking for each truck could be aggregated within seconds to spot emerging issues that affect many trucks and require a strategic response? These issues could include:
- Unexpected delays in a region due to highway blockages or weather that indicate the need to inform or reroute several trucks
- An unusually large number of soon-to-be timed-out drivers or impending maintenance issues which require making immediate schedule changes to avoid downtime
- Congregated drivers who are impacting on-time deliveries
The current telematics architecture also has inherent scalability issues in the form of network bottlenecks. Because all telemetry is stored in the in-memory data grid and accessed by a separate farm of compute servers, the network between the grid and the server farm can quickly bottleneck as the incoming message rate increases. As the fleet size grows and the message rate per truck increases from once per minute to once per second, the telematics system may not be able to handle the additional incoming telemetry.
Solution: Real-Time Digital Twins
A new software architecture for streaming analytics based on the concept of real-time digital twins can address these challenges and add significant capabilities to telematics systems. This new, object-oriented software technique provides a memory-based orchestration framework for tracking and analyzing telemetry from each data source. It comprises message-processing code and state variables which host dynamically evolving contextual information about the data source. For example, the real-time digital twin for a truck could look like this:
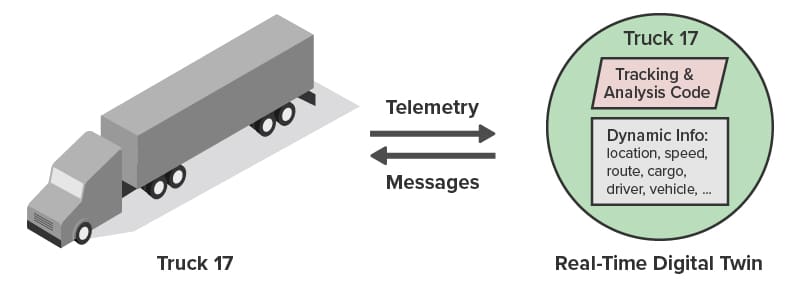
Instead of just snapshotting incoming telemetry, real-time digital twins for every data source immediately analyze it, update their state information about the truck’s condition, and send out alerts or commands to the truck or to managers as necessary. For example, they can track engine telemetry with knowledge of the engine’s known issues and maintenance history. They can track position, speed, and acceleration with knowledge of the route, schedule, and driver (allowed time left, driving record, etc.). Message-processing code can incorporate a rules engine or machine learning to amplify their capabilities.
Real-time digital twins digest raw telemetry and enable intelligent alerting in the moment that assists both drivers and dispatchers in surfacing issues that need immediate attention. They are much easier to develop than typical streaming analytics applications, which have to sift through the telemetry from all data sources to pick out patterns of interest and which lack contextual information to guide them. Because they are implemented using in-memory computing techniques, real-time digital twins are fast (typically responding to messages in a few milliseconds) and transparently scalable to handle hundreds of thousands of data sources and message rates exceeding 100K messages/second.
Here’s a depiction of real-time digital twins running within an in-memory data grid in a telematics architecture:
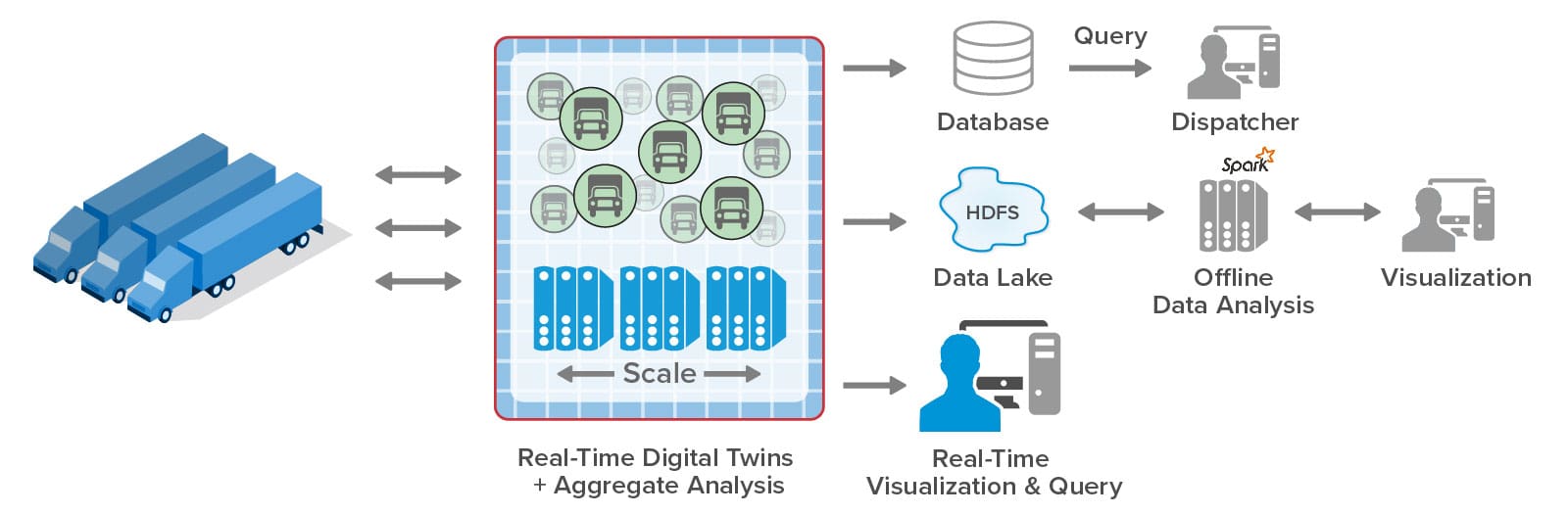
In addition to fitting within an overall architecture that includes database query and offline analytics, real-time digital twins enable built-in aggregate analytics and visualization. They provide curated state information derived from incoming telemetry that can be continuously aggregated and visualized to boost situational awareness for managers, as illustrated below. This opens up an important new opportunity to aggregate performance indicators needed in real time, such as emerging road delays by region or impending scheduling issues due to timed out drivers, that can be acted upon while new problems are still nascent. Real-time aggregate analytics add significant new capabilities to telematics systems.
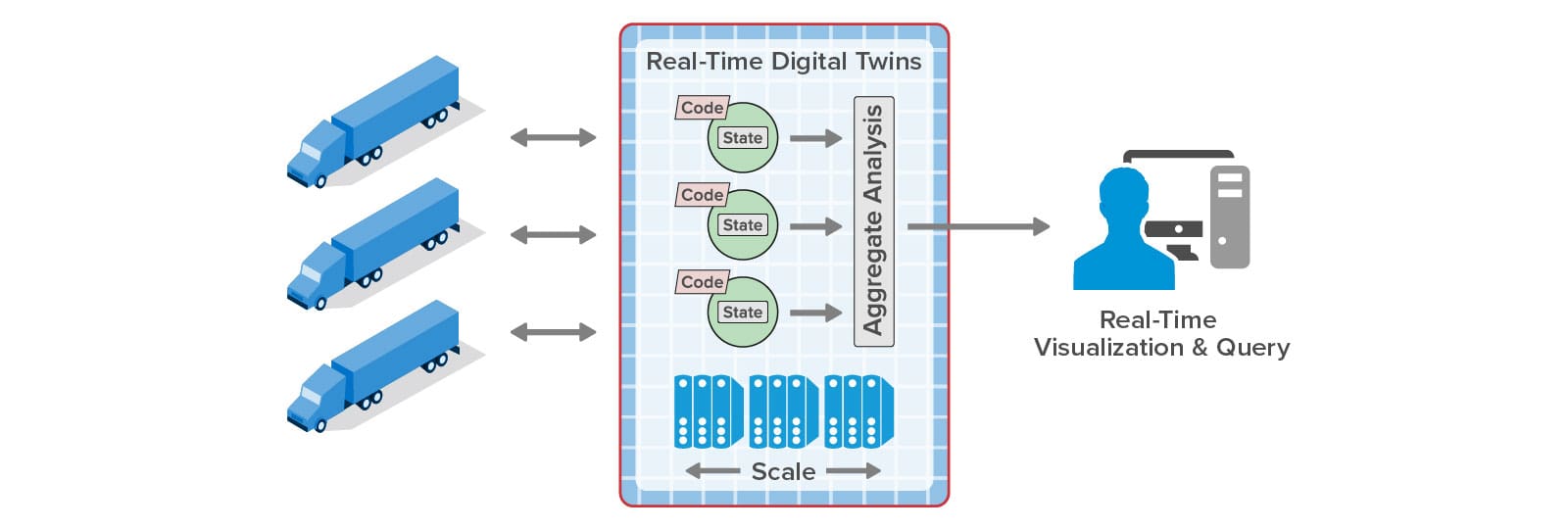
Summing Up
While telematics systems currently provide a comprehensive feature set for managing fleets, they lack the important ability to track and analyze telemetry from each vehicle in real time and then aggregate derived information to maintain continuous situational awareness for the fleet. Real-time digital twins can address these shortcomings with a powerful, fast, easy to develop, and highly scalable software architecture. This new software technique has the potential to make a major impact on the telematics industry.
To learn more about real-time digital twins in action, take a look at ScaleOut Software’s streaming service for hosting real-time digital twins in the cloud or on-premises here.
The post Use Digital Twins for the Next Generation in Telematics appeared first on ScaleOut Software.
]]>The post ScaleOut Discusses Contact Tracing in The Record appeared first on ScaleOut Software.
]]>Also read our Partner Perspective in the same issue, which explains how the Microsoft Azure cloud provides a powerful platform for hosting the ScaleOut Digital Twin Streaming Service and ensures high performance across a wide range of applications.
and ensures high performance across a wide range of applications.
The post ScaleOut Discusses Contact Tracing in The Record appeared first on ScaleOut Software.
]]>The post ScaleOut Software Releases New Video on Real-Time Digital Twins appeared first on ScaleOut Software.
]]>
Check out this new video which depicts the challenges in using conventional tools for streaming analytics to track and respond to thousands of data sources in a live system. Whether you are keeping track of a fleet of trucks or sensors in a smart city, the overwhelming amount of incoming telemetry from countless data sources can create a “data monster” that threatens your ability to perform real-time monitoring and maintain the necessary situational awareness.
As the video shows, ScaleOut’s real-time digital twins running in the ScaleOut Digital Twin Streaming Service can tame your data monster by separately tracking each data source using dynamic state information. They enable fast introspection on dynamic changes and immediate, focused responses. In addition, real-time digital twins continuously gather information which the streaming service can aggregate and visualize in real time to quickly surface issues and enable strategic responses.
can tame your data monster by separately tracking each data source using dynamic state information. They enable fast introspection on dynamic changes and immediate, focused responses. In addition, real-time digital twins continuously gather information which the streaming service can aggregate and visualize in real time to quickly surface issues and enable strategic responses.
Grab your popcorn and then click on the image below to watch the video:
We hope you enjoyed the video. Here’s how to learn more:
- To learn more about the value of real-time digital twins in streaming analytics, click here.
- To learn more about the ScaleOut Digital Twin Streaming Service, click here.
- For detailed technical information, take a look at the User Guide here.
- To contact us and talk about how real-time digital twins can help tame your data monster, click here.
The post ScaleOut Software Releases New Video on Real-Time Digital Twins appeared first on ScaleOut Software.
]]>The post Founder & CEO William Bain Discusses Real-Time Digital Twins with TechStrong TV appeared first on ScaleOut Software.
]]>Watch the video here.

The post Founder & CEO William Bain Discusses Real-Time Digital Twins with TechStrong TV appeared first on ScaleOut Software.
]]>The post ScaleOut Software Releases COVID-19 Corporate Contact Tracing Demonstration Application appeared first on ScaleOut Software.
]]> to Track Real-Time Data and Help Companies Safely Return to the Office
to Track Real-Time Data and Help Companies Safely Return to the Office
BELLEVUE, Wash – August 25, 2020 – ScaleOut Software today released a corporate contact tracing demonstration application to help companies safely return to the office during the COVID-19 pandemic. The application uses the ScaleOut Digital Twin Streaming Service and an associated mobile app to help businesses track thousands of daily interactions among employees and promptly notify them when a possible exposure to COVID-19 occurs.
and an associated mobile app to help businesses track thousands of daily interactions among employees and promptly notify them when a possible exposure to COVID-19 occurs.
The contact tracing application makes use of new software technology for streaming analytics that enables thousands of data sources to be tracked simultaneously. It creates a “real-time digital twin” for each employee to track their contacts within the organization. When any employee reports a positive COVID-19 result, these real-time digital twins can quickly and easily notify other employees who could have been exposed and require testing. The application also removes non-recurring contacts after exposure is no longer likely.
“Since ScaleOut Software’s founding nearly two decades ago, we have continually advanced our streaming analytics technology to help customers tackle complex problems and now to help respond to the COVID-19 pandemic,” said Dr. William Bain, ScaleOut Software’s CEO and founder. “Our contact tracing application should prove highly valuable in precisely identifying affected employees and enabling quick action to contain an outbreak across work environments.”
Using Real-Time Digital Twins for Corporate Contact Tracing
ScaleOut Software’s contact tracing application using real-time digital twins runs on the Microsoft Azure cloud and connects to a companion mobile app used by employees. It was designed to be easily integrated into an organizational database and is customizable to meet the specific needs of each company.
Key benefits include:
- Simultaneously Tracks Thousands of Employees: The application automatically tracks the most common infection scenarios by using the company’s employee database to connect colleagues who work in the same department and interact daily.
- Easy to Use Mobile Application: Employees need only to manually log contacts they make with people in outside departments to assist with the contact tracing. These interactions are relatively infrequent and are tracked for about two weeks.
- Notifies Affected Individuals in Seconds: When an employee notifies the mobile app of a positive test for COVID-19, a chain of communication promptly alerts everyone in the corporate environment who has direct or indirect connections with that person.
- Spots Emerging Outbreaks: Managers can use aggregate analytics to visualize and identify emerging trends in seconds. For example, they can display the number of positive COVID-19 reports and the number of affected employees by department or location. This enables managers to isolate hot spots within a company and take steps to reduce the likelihood of future outbreaks.
- Helps Local Communities: Employees can also manually track information about the contacts they make while on business travel, such as during airline flights, taxi rides, and meals at restaurants. This option enables companies to assist their communities in contact tracing and to help contain the spread of COVID-19.
For more information, please visit www.scaleoutsoftware.com and follow @ScaleOut_Inc on Twitter.
Additional Resources:
- COVID-19 Corporate Contact Tracing Blog Post
- ScaleOut Digital Twin Streaming Service Product Page
About ScaleOut Software
Founded in 2003, ScaleOut Software develops leading-edge software that delivers scalable, highly available, in-memory computing and streaming analytics technologies to a wide range of industries. ScaleOut Software’s in-memory computing platform enables operational intelligence by storing, updating, and analyzing fast-changing, live data so that businesses can capture perishable opportunities before the moment is lost. It has offices in Bellevue, Washington and Beaverton, Oregon.
###
Contact:
RH Strategic for ScaleOut Software
The post ScaleOut Software Releases COVID-19 Corporate Contact Tracing Demonstration Application appeared first on ScaleOut Software.
]]>The post Using Real-Time Digital Twins for Corporate Contact Tracing appeared first on ScaleOut Software.
]]>
Until a COVID-19 vaccine is widely available, getting back to work means keeping a close watch for outbreaks and quickly containing them when they occur. While the prospects for accomplishing this within large companies seem daunting, tracking contacts between employees may be much easier than for the public at large. This blog post explains how a software application built with a new software construct called real-time digital twins makes this possible.
Tracking Employees Using Real-Time Digital Twins
In an earlier blog post, we saw how real-time digital twins running in the ScaleOut Digital Twin Streaming Service can be used to track employees within a large company using a technique called “voluntary self-tracing.” In this post, we’ll take a closer look at its implementation in a demo application created by ScaleOut Software. We’ll also look at a companion mobile app that allows employees to log contacts with colleagues outside their immediate teams and to notify the company and their contacts if they test positive for COVID-19.
can be used to track employees within a large company using a technique called “voluntary self-tracing.” In this post, we’ll take a closer look at its implementation in a demo application created by ScaleOut Software. We’ll also look at a companion mobile app that allows employees to log contacts with colleagues outside their immediate teams and to notify the company and their contacts if they test positive for COVID-19.
The demo application creates a memory-based real-time digital twin for each employee. Using information from the company’s organizational database, it populates each twin with the employee’s ID, team ID, department type, and location. The twin also keeps a list of the employee’s contacts within the organization (as well as community contacts, discussed below). This allows immediate colleagues and their contacts to be notified if an employee tests positive. The following diagram illustrates an employee’s real-time digital twin and the state data it holds; details about the contact tracing code are explained below:
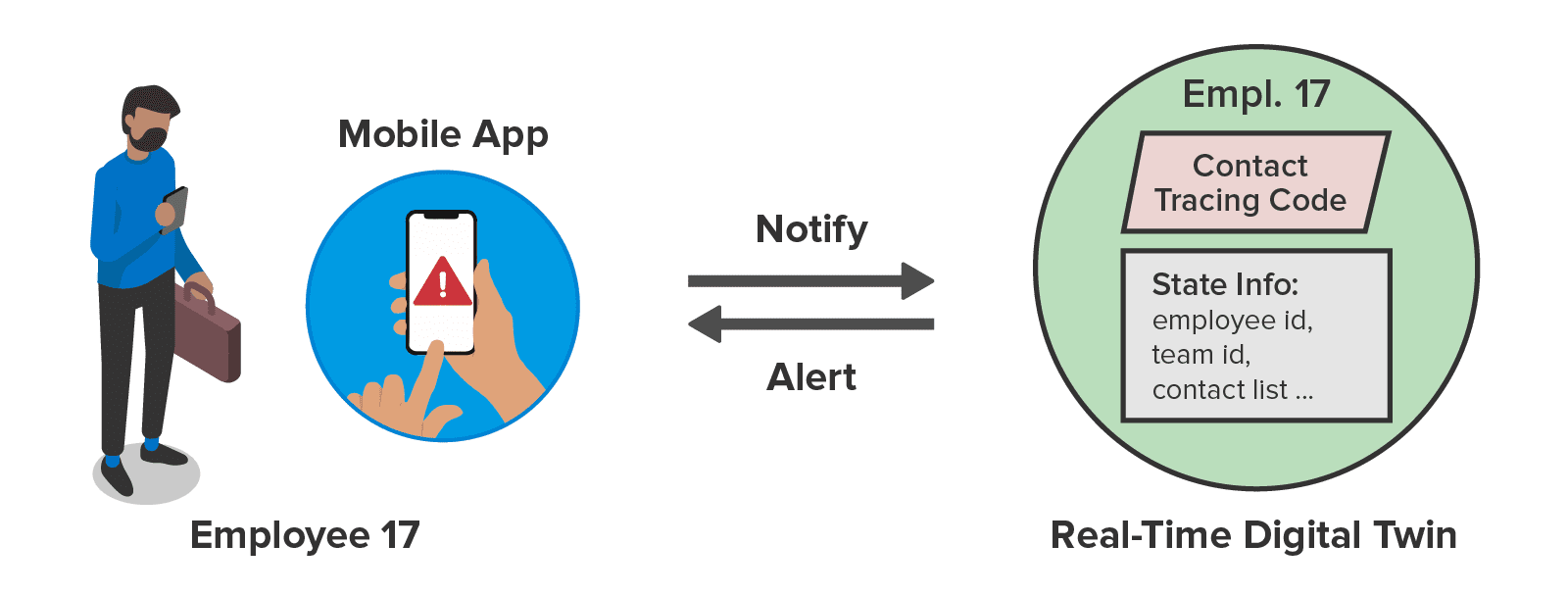
The twin automatically populates its contact list with the other members of the employee’s team, based on the expectation that team members are in daily contact. Using the mobile app, employees can log one-time and recurring contacts with colleagues in other teams, possibly at different office locations. In addition, they can log contacts outside the company, such as taxi rides, airline flights, and meals at restaurants, so that community members can be notified if an employee was exposed to COVID-19.
An employee can use the mobile app to notify their real-time digital twin of a positive test for COVID-19. Code running in the twin then sends messages to the real-time digital twins for all contacts in the employee’s list. These twins in turn send messages to their contacts, and so on, until the twins for all contacts have been notified. (The algorithm avoids unnecessary messages to team members and circular paths among twins.) The twin then sends a push notification to each affected employee through the mobile app, alerting them to the possible exposure and the number of intermediate contacts between themselves and the infected person. Because real-time digital twins are hosted in memory, all of this happens within seconds, enabling affected employees to immediately self-quarantine and obtain COVID-19 tests.
Here’s an illustration of the chain of contacts originating with an employee who reports testing positive. (Note that the outbound notifications from the twins to the employees’ mobile devices are not shown here.)
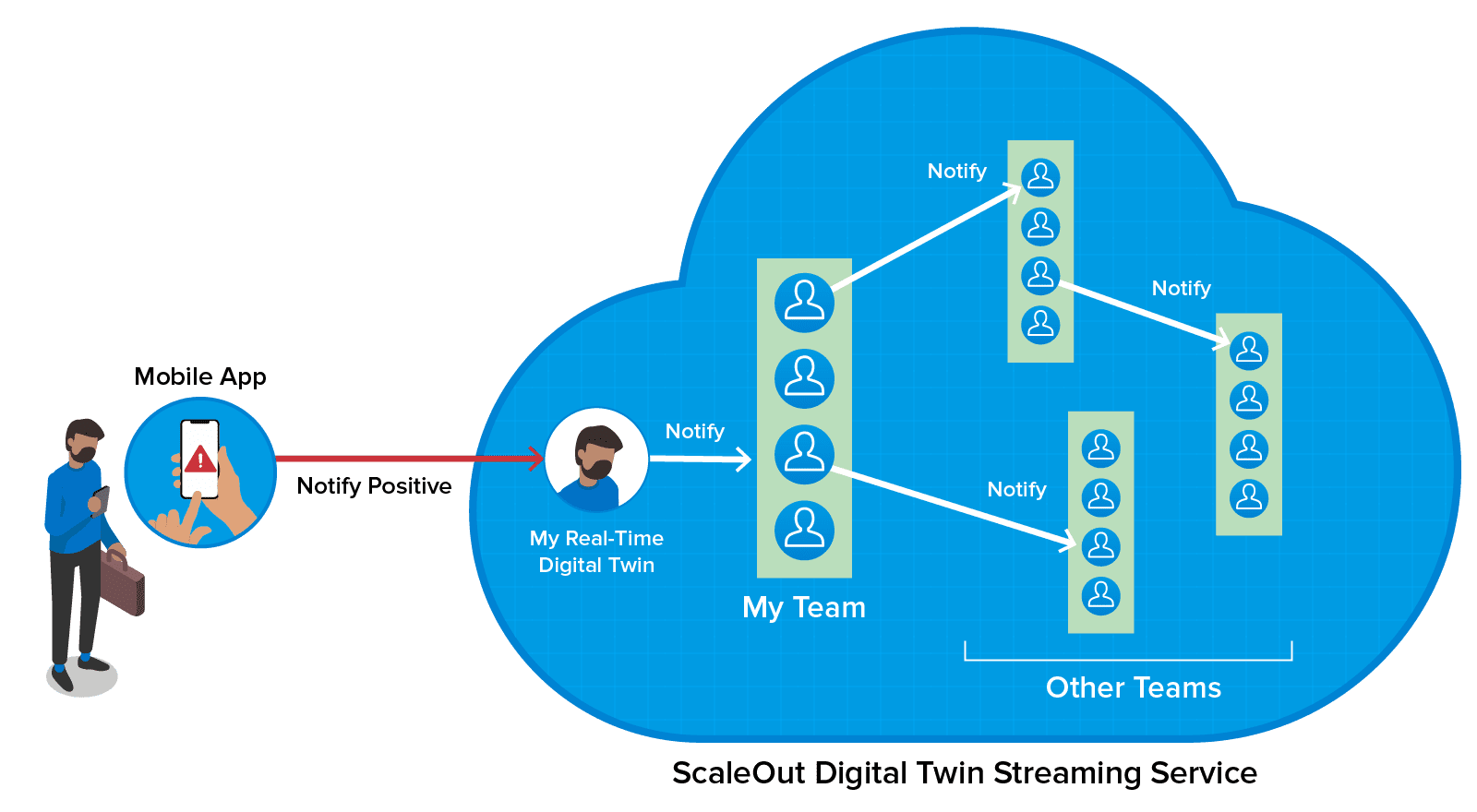
What’s in the Real-Time Digital Twin?
As illustrated in the first diagram, each real-time digital twin hosts two components, state data and a message-processing method. These are defined by the contact tracing application and can be written in C#, Java, or JavaScript. (C# was used for the demo application.) The state data is unique for each employee and contains the employee’s information and contact list, along with useful statistics, such as how often the employee has been alerted about a possible exposure. The message-processing method’s code is shared by all twins. It receives messages from the mobile app or from other twins (each corresponding to a single employee) and uses application-defined code to process these messages.
Messages from the mobile app can request to add or remove a contact from the list. For new contacts, they include parameters such as the employee ID of the contact and whether the contact will be recurring. (Users also can record contacts using calendar events.) Messages from the mobile app can also request the current contact list for display, signal that the employee has tested positive or negative, and request current notifications. Messages from other real-time digital twins signal that the corresponding employees have been exposed and provide additional information, such as the number of intermediate contacts and the location of the initial employee who tested positive.
The application’s message-processing code responds to these messages and implements the spanning-tree notification algorithm that alerts other twins on the contact list. The streaming service handles the rest, namely the details of message delivery, retrieval and updating of state information, and managing the execution platform.
Using the Mobile App
The following animated diagram shows how an employee can add a contact with a company colleague outside of their immediate team or with a community contact during business travel (left screenshot). If the employee tests positive, the employee can use the mobile app to report this to the company (middle screenshot). All employees are then notified using the mobile app, as shown in the right screenshot. Community contacts are reported to managers who communicate with outside points of contact, such as airlines, taxi companies, and restaurants.
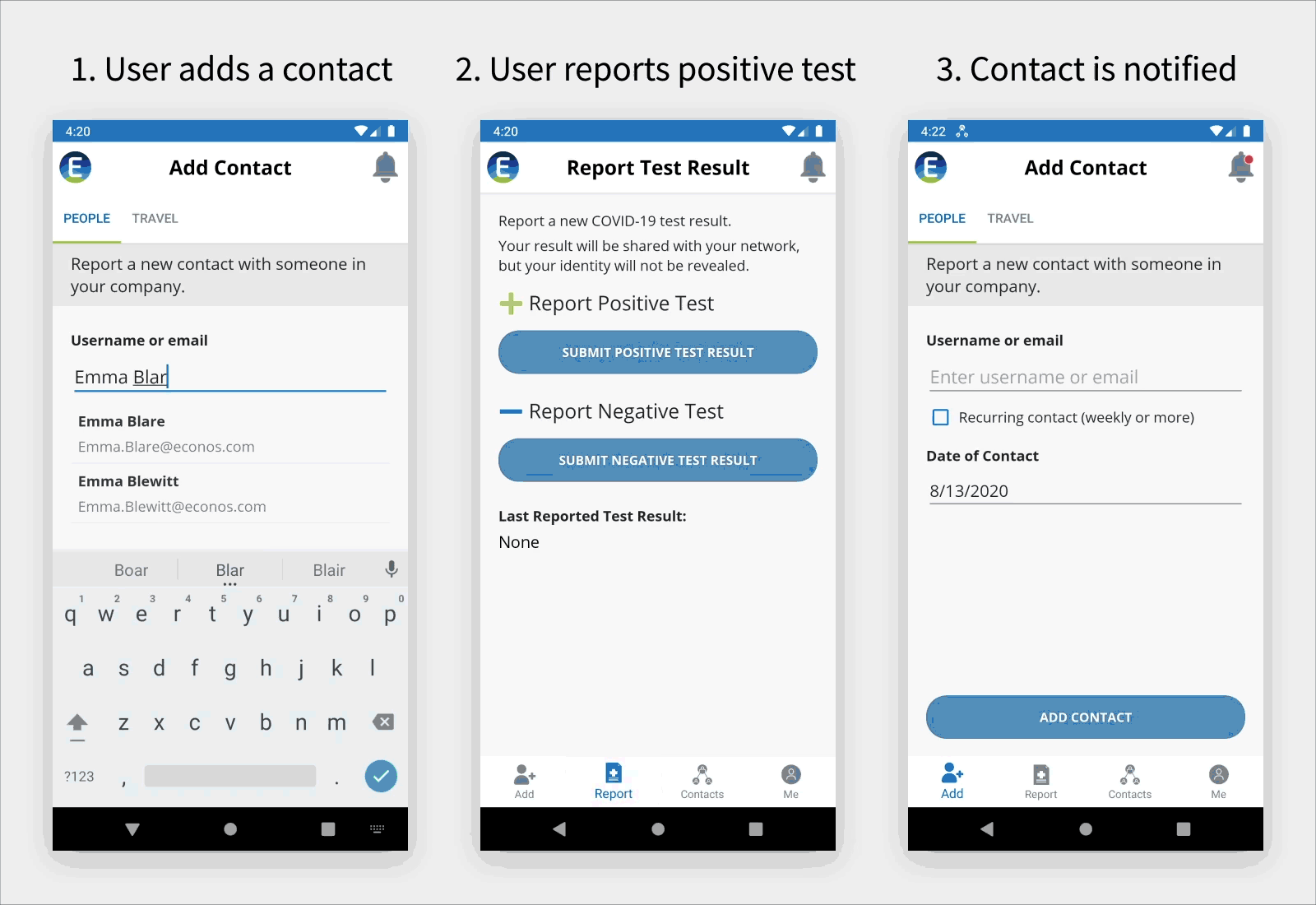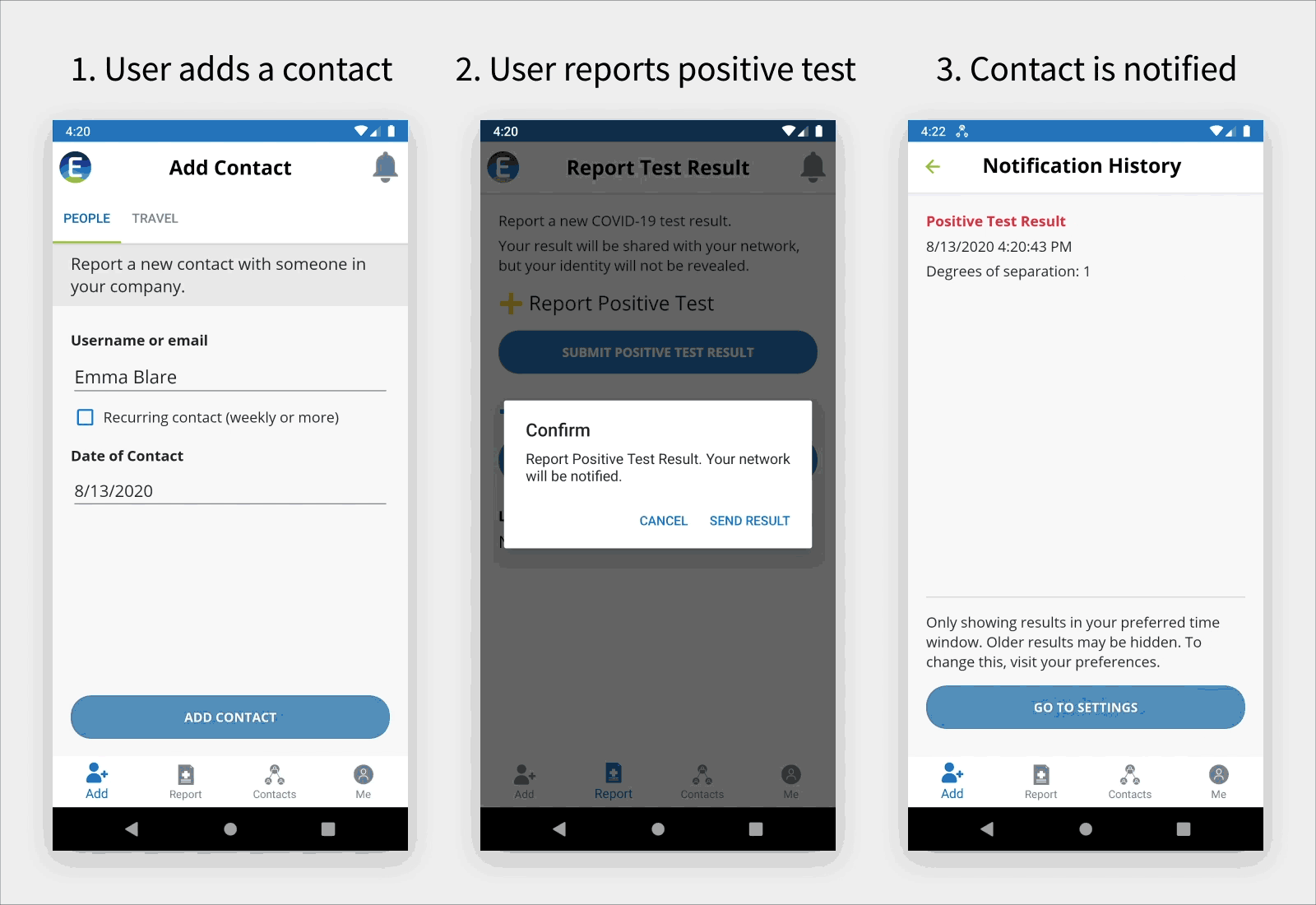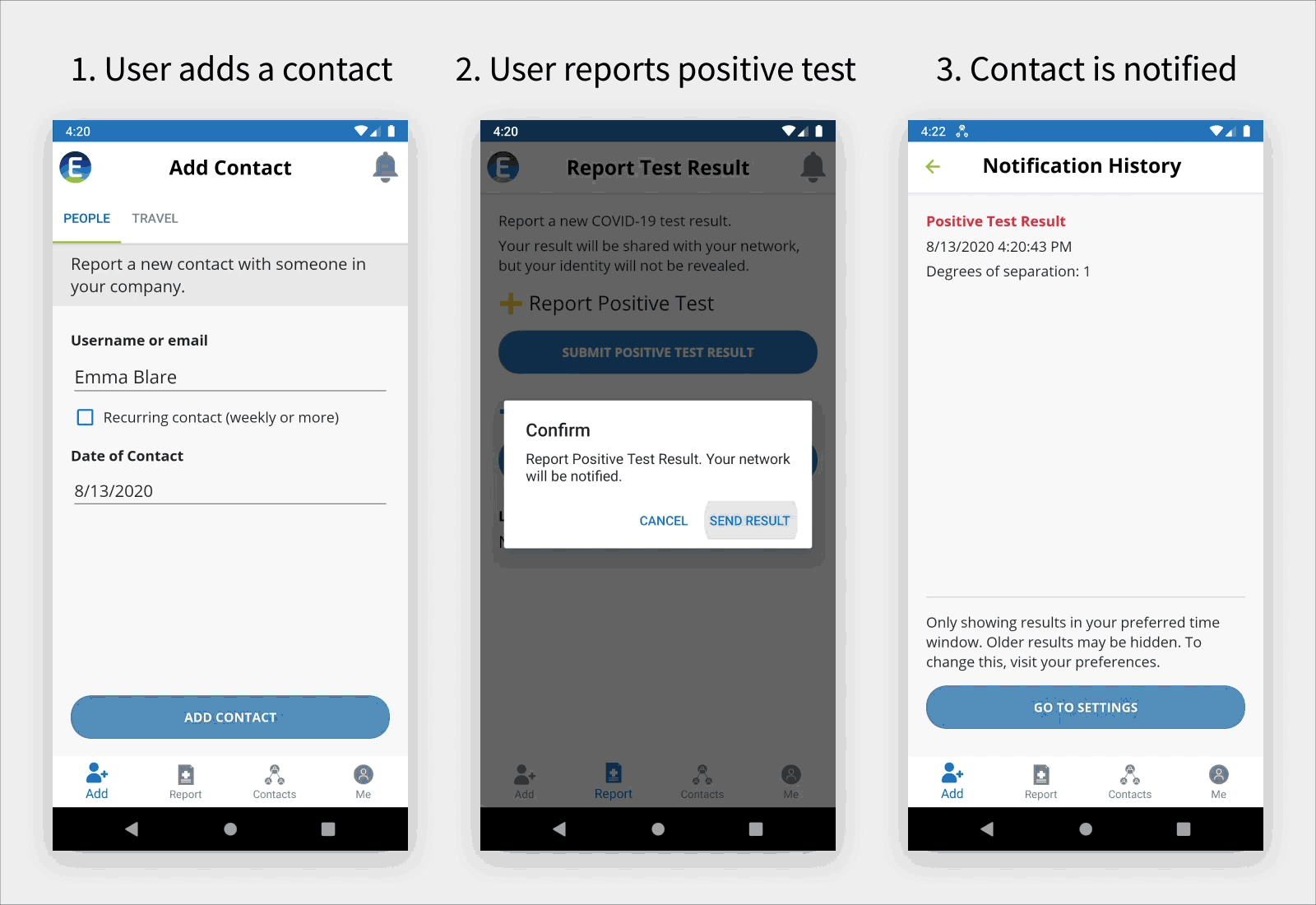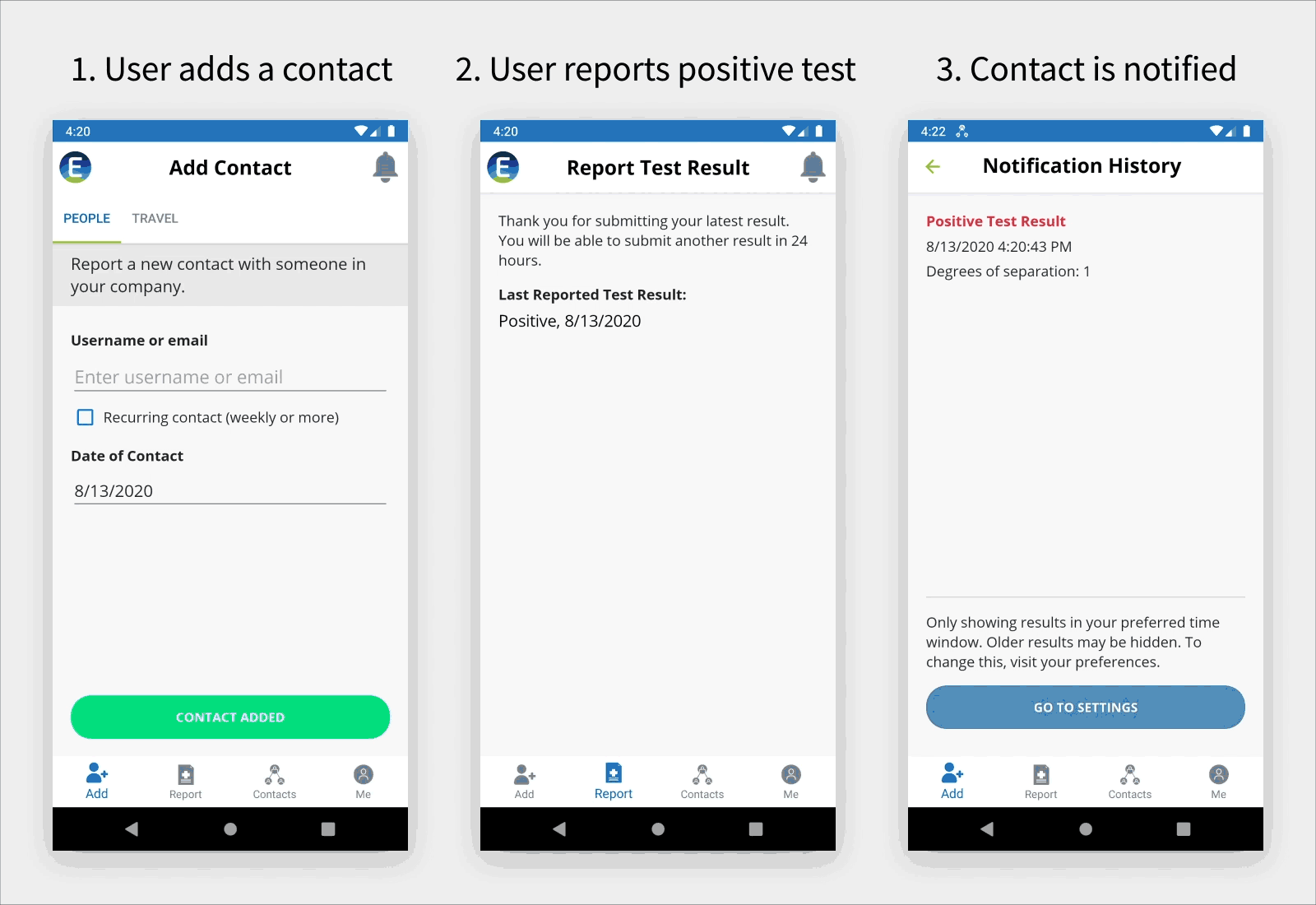
Using Aggregate Statistics to Spot Outbreaks
The streaming service has the built-in capability to aggregate state data from all real-time digital twins. The service then displays the results in charts which are recalculated every few seconds. These charts enable managers to identify emerging issues, such as an outbreak within a specific department or site. With this information, they can take immediate steps to contain the outbreak and minimize the number of affected employees.
To illustrate the value of aggregate statistics in boosting situational awareness, consider a hypothetical company with 30,000 employees and offices in several states across the U.S. Suppose an employee at the Texas site suddenly tests positive. This could be immediately alerted to managers with the following chart generated and continuously updated by the streaming service, which shows all employees who have tested positive:
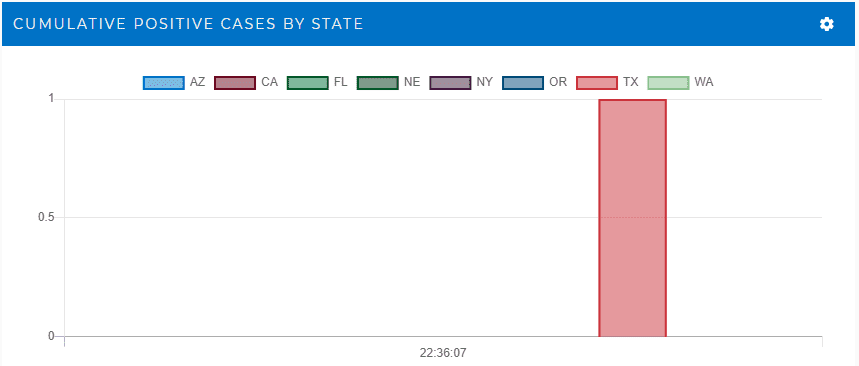
Within a few seconds, the real-time digital twins notify all points of contact. Updates to state data are immediately aggregated in another chart that shows the sites where employees have been notified of a positive contact and the number of employees affected at each site:
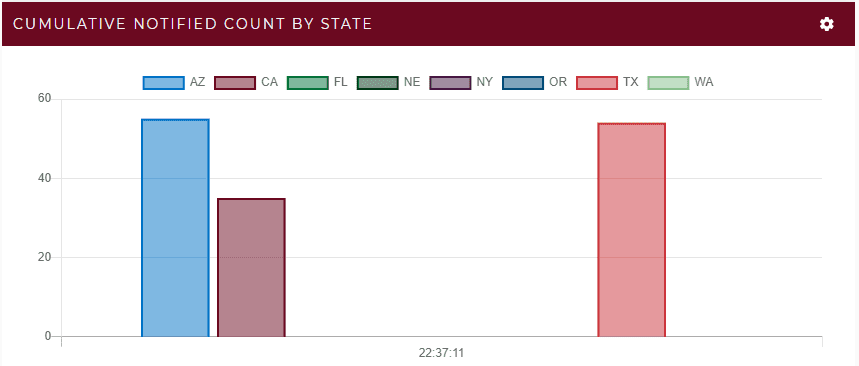
This chart shows that about 140 employees in three states were notified and possibly exposed directly or indirectly. All of these employees are then immediately quarantined to contain the possible spread of COVID-19. After an investigation by company managers, it is determined that the employee had business travel to Arizona and met with a team that subsequently had business travel to California. Instead of taking hours or days to uncover the scope of a COVID-19 exposure, contact tracing using real-time digital twins alerts managers within seconds.
The real-time digital twins can collect additional useful statistics for visualization by the streaming service. Another chart can show the average number of intermediate contacts for all notified employees, which is an indication of how widely employees have been interacting across teams. If this becomes an issue (as it is in the above example), managers can implement policies to further isolate teams. As shown below, a chart can also show the number of notified employees by department so that managers can determine whether certain departments, such as retail outlets, need stricter policies to limit exposure to COVID-19 from outside contacts.
The Benefits of an Integrated Streaming Service
This contact tracing application demonstrates the power of real-time digital twins to enable fast application development with compelling benefits. Because the amount of application code is small, real-time digital twins can be quickly written and tested. (See a recent blog post which describes how to simplify debugging and testing using a mock environment prior to deployment in the cloud.) They also can be easily modified and updated.
The ScaleOut Digital Twin Streaming Service provides the execution platform so that the application code does not have to deal with message distribution, state saving, performance scaling, and high availability. It also includes support for real-time aggregate analytics and visualization integrated with the real-time digital twin model to maximize ease of use.
Compare this approach to the complexity of building out an application server farm, database, analytics application, and visualization to accomplish the same goals at higher cost and lower performance. Cobbling together these diverse technologies would require several skill sets, lengthy development time, and higher operational costs.
Summing Up
This demo contact tracing application was designed to show how companies can take advantage of their organizational structures to track contacts among employees and quickly notify all affected employees when an individual tests positive for COVID-19. By responding quickly to an exposure with immediate, comprehensive information about its extent within the company (and with community contacts), managers can limit the exposure’s impact. The application also shows how the real-time digital twin model enables a quick, agile implementation which can be easily adapted to the specific needs of a wide range of companies.
Please contact us at ScaleOut Software to learn more about this demo application for limiting the impact of COVID-19 and other ways real-time digital twins can help your company monitor and respond to fast-changing events.
The post Using Real-Time Digital Twins for Corporate Contact Tracing appeared first on ScaleOut Software.
]]>